Motions of the Earth Class 6 Extra Questions Social Science Geography Chapter 3
NCERT Extra Questions for Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth
Motions of the Earth Class 6 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Define rotation and revolution of the Earth.
Answer:
Rotation:
Movement of the Earth on its axis in nearly 24 hours is termed as rotation. It is also called the daily movement of the earth.
Revolution:
Movement of the earth around the Sun on a fixed path or orbit is called revolution.
Question 2.
What are axis and orbit?
Answer:
Axis:
The axis of the Earth is an imaginary line joining the North pole with the South pole. It makes an angle of 6614° with its orbital plane.
Orbit:
Orbit is the elliptical path on which heavenly bodies move around their sun or planet.
Question 3.
What is the circle of illumination? Why does it not coincide with the axis of the Earth?
Answer:
- The circle which separates day from night is called the circle of illumination.
- This circle does not coincide with the axis because of the inclination of the axis by 2314° towards east.
- The earth takes 24 hours (one day) to complete one rotation around its axis.
Motions of the Earth Class 6 Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Distinguish between rotation and revolution.
Answer:
The distinction between rotation and revolution is as under:
Rotation. | Revolution |
| 1. The spinning of the Earth on its axis is called rotation. | 1. Annual motion of the Earth round the Sun is called revolution. |
| 2. The time of rotation is about 24 hours. | 2. The time of revolution is 365 days 6 hours. |
| 3. Days and nights follow each other in regular succession in all parts of the Earth due to rotation. | 3. The change of season takes place the revolution of the Earth. |
Question 2.
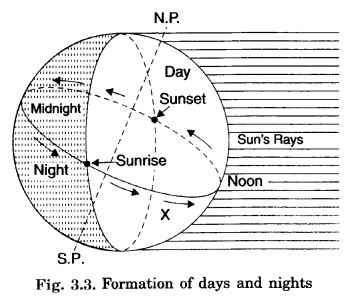
How are days and nights formed?
Answer:
- The earth receives light from the Sun.
- Because of its spherical shape; only half of it gets light from the Sun at a time.
- The portion facing the Sun experiences daytime while the other portion away from the Sun experiences night.
Motions of the Earth Class 6 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Explain the following:
- Revolution of the Earth.
- Leap year.
Answer:
1. Revolution of the Earth:
- Earth’s movement around the Sun on its orbit is called revolution.
- The earth takes 36514 days (one year) to revolve round the Sun.
- We take a year of 365 days only and ignore 6 hours for the sake of convenience.
2. Leap Year:
- Six hours saved every year in revolution are added for four years.
- They become 24 hours or one additional day.
- The day is added to the month of February every four years.
- It is because of this that every fourth year February has one more day – 29 days instead of 28 days.
- Such a year of 366 days is called a leap year.
Question 3.
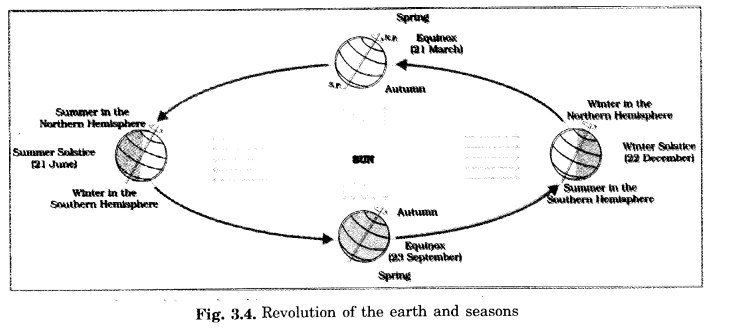
How are seasons caused?
Answer:
- The Earth revolves round the Sun on an elliptical orbit.
- Its axis is inclined in the same direction (east) on its orbit by 2314°.
- The revolution of the Earth and the inclination of the earth’s axis in a fixed direction cause seasons.
- A year is divided into four seasons.
- They are Spring, Summer, Autumn and Winter.
- Seasons change with the change in the position of the Earth around the Sun.
On 21st June, Northern hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun.
- On that day the Sun shines directly on the Tropic of Cancer (231/2° N). Hence, these areas receive more heat.
- The areas near the poles receive less heat because the rays of the Sun are slanting there.
- The North hemisphere is inclined towards the Sun and the places beyond the Arctic Circle experience continuous day light.
- As a large portion of the Northern hemisphere gets light from the Sun, therefore, it is Summer in the Northern hemisphere.
- The duration of day is longer and that of night shorter here.
At this time in the Southern hemisphere all these conditions are opposite.
- It is winter season there.
- Nights are longer than days.
- This position of the Earth is called summer solstice.
On 22nd December, the Tropic of Capricorn receives the direct rays of the Sun and Southern hemisphere tilts towards it.
- On this day the Sun shines vertically on the Tropic of Capricorn (23W S).
- Hence a larger portion of the Southern Hemisphere gets light.
- It is summer in the Southern hemisphere with longer days and shorter nights.
- The opposite conditions are prevalent in the Northern hemisphere.
- This position of the Earth is called winter solstice.
On 21 March and 23 September, The Sun shines vertically on the equator.
- In this position neither of the hemispheres is tilted towards the Sun, so the whole of the Earth experiences equal days and equal nights.
- It is neither very cold nor very hot all over the world.
- The Northern hemisphere experiences spring on 21st March and autumn on 23rd September.
- Exactly the opposite happens in the Southern hemisphere. Here, it is spring on September 23rd and autumn on March 21st.
- These positions are called Spring and Autumn Equinoxes respectively.
Motions of the Earth Class 6 Extra Questions Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Motion of the earth on its axis in about 24 hours is called
(a) revolution
(b) rotation
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
rotation
Question 2.
Motion of the earth around the sun is known as
(a) revolution
(b) rotation
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
revolution
Question 3.
What is orbital plane?
(a) Plane formed by the axis
(b) Plane formed by the orbit
(r) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
Plane formed by the orbit
Question 4.
Which one of the following is the source of light on the earth?
(a) The moon
(b) The sun
(c) The satellite
(d) The space
Answer:
The sun
Question 5.
The circle that divides the globe into day and night is called
(a) circle of darkness
(b) circle of day and night
(c) circle of illumination
(d)none of these
Answer:
circle of illumination
Question 6.
The period of one rotation of the earth is known as
(a) the sun day
(b) the moon day
(c) the earth day
(d) none of these
Answer:
the earth day
Question 7.
What would have happened if the earth did not rotate?
(a) Cold conditions on earth’s half portion
(b) Warm conditions on earth’s another half portion
(c) No life possible in such extreme conditions
(d) All of these
Answer:
All of these
Question 8.
A year with 366 days is called
(a) leap year
(b) normal year
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
leap year
Question 9.
Why do seasons change on the earth?
(a) Due to change in the position of the earth around the sun
(b) Due to no change in the earth’s position
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
Due to change in the position of the earth around the sun
Question 10.
When do the longest day and the shortest night occur in the northern hemisphere?
(a) June 21
(b) September 23
(c) December 22
(d) March 21
Answer:
June 21
Question 11.
In which season Christmas is celebrated in Australia?
(a ) Winter season
(b) Summer season
(c) Autumn season
(d) Spring season
Answer:
Summer season
Question 12.
When do equinoxes occur on the earth?
(a) March 21
(b) September 23
(c) Both (a) and (6)
(d ) None of these
Answer:
Both (a) and (6)
Question 13.
Days and nights occur on earth due to
(a) rotation
(b) revolution
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
rotation
Question 14.
Change of seasons occurs on earth due to
(a) rotation
(b) revolution
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
revolution










