- Basic Geometrical Ideas Exercise 4.1
- Basic Geometrical Ideas Exercise 4.2
- Basic Geometrical Ideas Exercise 4.3
- Basic Geometrical Ideas Exercise 4.4
- Basic Geometrical Ideas Exercise 4.5
- Basic Geometrical Ideas Exercise 4.6
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas Ex 4.6
Exercise 4.6
Ex 4.6 Class 6 Maths Question 1.
From the figure, identify:
(a) the centre of circle
(b) three radii
(c) a diameter
(d) a chord
(e) two points in the interior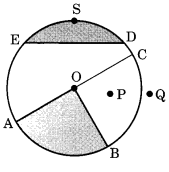
(f) a point in the exterior
(g) a sector
(h) a segment.
Solution:
In the given figure,
(a) O is the centre of the circle.
(b) Three radii of the given circle are
(c)
(d)
(e) O and P are in the interior of the circle.
(f) Q is a point in the exterior of the circle.
(g) OBA is a sector of the circle.
(h) EDSE, the shaded region is a segment of the circle.
Ex 4.6 Class 6 Maths Question 2.
(a) Is every diameter of a circle also a chord?
(b) Is every chord of a circle also a diameter?
Solution:
(a) Yes, every diameter is the longest chord of a circle.
(b) No, every chord is not diameter of a circle.
Ex 4.6 Class 6 Maths Question 3.
Draw any circle and mark
(a) its centre
(b) a radius
(c) a diameter
(d) a sector
(e) a segment
(f) a point in its interior
(g) a point in its exterior
(h) an arc.
Solution:
In the given circle,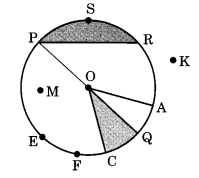
(a) O is the center.
(b)
(c)
(d) OQC is a sector (shaded part)
(e) PSR (shaded part) in the segment.
(f) M is in the interior of the circle.
(g) K is in the exterior of the circle.
(h)
Ex 4.6 Class 6 Maths Question 4.
Say ‘true’ or ‘false’.
(a) Two diameters of a circle will necessarily intersect.
(b) The centre of a circle is always in its interior.
Solution:
(a) True
(b) True













