Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Important Questions Science Chapter 1
Question 1:
Answer the following questions.
- Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature ?
- Name the two gases which are supplied in compressed form in homes and hospitals.
- What is dry ice ? (CBSE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
- The three states of matter are : solid, liquid and gas. Out of these, the solid state is the most rigid since the particles present are very closely packed and interparticle forces are quite strong.
- LPG (Liquid Petroleum Gas) is supplied in homes while liquefied oxygen in hospitals
- Solid carbon dioxide (CO2) is known as dry ice. It is so named as it does not wet a piece of paper or cloth.
Question 2:
CO2 is a gas. Justify the given statement by two reasons. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
- CO2 does not have a fixed volume. It can be compressed on applying pressure.
- CO2 does not have a fixed shape. It can take the shape of any container in which it is put.
Question 3:
What is a pure substance ? Give its one characteristic. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
A pure substance is the one which cannot be separated into smaller parts by any physical methods. It may be either a pure element (e.g. sodium) or a pure compound (e.g. calcium carbonate).
Question 4:
What happens when you pour some acetone on your palm ? (CBSE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
Acetone is a very low boiling liquid. It immediately changes to vapours. The evaporation is an endothermic process. Acetone takes up heat energy from hand. Therefore, the palm immediately becomes cold or even numb.
Question 5:
Name SI unit of measuring temperature. The boiling point of water is 100°C under normal atmospheric pressure. Convert this temperature to SI Units. (CBSE 2011, 2016)
Answer:
SI units of temperature is Kelvin (K)
100°C = (100 + 273) = 373 K.
Question 6:
Give reasons for the following :
(a) Gases fill up completely the vessel in which they are kept.
(b) Gases exert pressure on the walls of the containing vessel. (CBSE 2011, 2012, 2014, 2016)
Answer:
(a) Particles constituting gases are very fast moving and diffuse at a fast speed. They therefore, readily fill up the vessel completely in which these are kept.
(b) Particles of gases collide against the walls of the containing vessel and impart momentum to them. This is responsible for the pressure of the gas.
Question 7:
Name three states of matter. Which state of matter is rigid and why ? (CBSE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
The three states of matter are : solid, liquid and gas. Out of these, the solid state is the most rigid since the particles present are very closely packed and interparticle forces are quite strong.
Question 8:
What is meant by particulate nature of matter ? List four characteristics of particle nature of matter.
Answer:
In order to illustrate the particle nature of matter, take some water in a glass beaker. To this add one spoon full of some salt (e.g., sodium chloride) and stir with a glass rod.
The important characteristics of the particulate nature of matter may be summed up as follows :
- Every matter is made up of particles.
- The particles constituting a matter are very small in size.
- The particles have empty or vacant spaces in them known as interparticle spaces.
- Particles are not stationary and are in a state of motion.
- Attractive forces are present in the particles of a substance. These are called interparticle forces.
- The particle motion increases with the rise in temperature.
Question 9:
Why do people sprinkle water on a roof after a hot summer day ? (CBSE 2011, 2016)
Answer:
Water has a large heat of vaporisation. In a hot summer day, the roof is quite hot. Water absorbs a large amount of heat from the roof for its vaporisation. The roof gets sufficiently cool and one can sleep comfortably.
Question 10:
List three characteristics of particles of matter. Describe one example for each characteristic to illustrate it.
Name the characteristics which are responsible for
(a) spreading of smell of scent in a room and
(b) water taking the shape of the vessel in which poured. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
For the three characteristics of matter and their examples,
(a) Spreading of smell of scent in a room is because of diffusion of the gases. Scent consists of a number of sweet smelling gases or vapours.
(b) Water is a liquid and liquids take up the shape of any container in which these are kept.
Question 11:
The temperature-time graph given below shows the heating curve for pure wax. From the graph answer the following :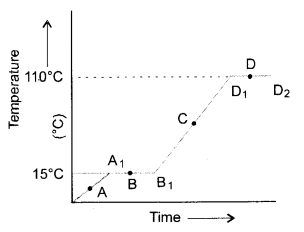
- What is the physical state of the substance at the points A, B, C and D ?
- What is the melting point of the substance ?
- What is its boiling point ?
- Which portions of the graph indicates that change of state is taking place.
- Name the terms used for heat absorbed during change of states involved in above processes. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
- At point A : Wax is in the solid state.
At point B : Wax has started melting and exists both in the solid as well as liquid states.
At point C : Wax is in liquid state.
At point D : Wax has started boiling. Therefore, it exists both in the liquid as well as gaseous states. - Melting point of wax = 15°C
- Boiling point of wax = 110°C
- The change of state (solid to liquid) is represented by the portion A1 to B2 (straight line).
The change of state (liquid to gas) is represented by the portion D1 to D2 (straight line). - It is known as latent heat of fusion in case of solids and latent heat of vaporisation in case of liquids.
Question 12:
Explain which one will cause more severe burns—boiling water at 100°C or steam at 100°C. (CBSE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
In order to illustrate the particle nature of matter, take some water in a glass beaker. To this add one spoon full of some salt (e.g., sodium chloride) and stir with a glass rod.
The important characteristics of the particulate nature of matter may be summed up as follows :
- Every matter is made up of particles.
- The particles constituting a matter are very small in size.
- The particles have empty or vacant spaces in them known as interparticle spaces.
- Particles are not stationary and are in a state of motion.
- Attractive forces are present in the particles of a substance. These are called interparticle forces.
- The particle motion increases with the rise in temperature.
Question 13:
On suffering from high fever, which will lower your body temperature more; ice or ice cold water ?
(CBSE 2012, 2014)
Answer:
Ice will lower the body temperature more than ice cold water because latent heat of fusion of ice is quite high (335 kj kg-1). Ice is therefore, expected to absorb more heat energy from the body and will lower the body temperature more than ice cold water.
Question 14:
Flow will you change water from gaseous state to liquid state ? Suggest a simple activity. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Pass the water vapours or steam through a water condenser as used in case of simple distillation. It gets condensed to form liquid water.
Question 15:
Justify that melting of wax is a physical change. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
It can be justified in two ways :
- No new substance is formed and there is no change in the chemical properties of wax as a result of melting.
- When the liquid wax is cooled for sometime, it again gets solidified.
Question 16:
Ramesh took two beakers A and B containing hot water and cold water respectively. In each beaker, he dropped a crystal of copper sulphate. He kept the beakers undisturbed. After sometime what did he observe and why ? (CBSE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
In both the beakers, the solutions became blue. However, this happened at a faster rate in the beaker B which contains hot water. This change has taken place because of the process of diffusion which proceeds at a faster rate in hot water as compared to cold water.
Question 17:
Archit dropped a crystal of potassium permanganate into two beakers A and B containing hot water and cold water respectively. After keeping the beakers undisturbed for some time what did he observe and why ?
(CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Potassium permanganate crystals have purple colour. In a beaker B containing hot water, the purple colour would spread more readily as compared to the beaker A which contains in it cold water. Actually the kinetic energy of the particles increases with the rise in temperature.
Question 18:
Account for the following ;
- When sugar crystals dissolve in water, the level of water does not rise appreciably.
- Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid residue.
- A wooden table should be called a solid.
- Dogs generally hang out their tongue in summer. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
- Since water is a liquid, there are intermolecular spaces. Sugar particles occupy these spaces. As a result, water
level does not rise appreciably, - A pure substance is the one which cannot be separated into smaller parts by any physical methods. It may be either a pure element (e.g. sodium) or a pure compound (e.g. calcium carbonate).
- For the three characteristics of matter and their examples,
- Spreading of smell of scent in a room is because of diffusion of the gases. Scent consists of a number of sweet smelling gases or vapours.
- Water is a liquid and liquids take up the shape of any container in which these are kept.
- In summer, dogs get exhausted due to the loss of persipiration from their body. Since they are always running most of the time, they hang out their tongue.
Question 19:
(a) 5 mL of water was taken in a test tube and china dish separately. These samples were then kept under different conditions as below :
(i) Both the samples are kept under a fan.
(ii) Both the samples are kept inside a cup board.
State in which case evaporation will be faster ? Give reason to support your answer.
(b) How will the rate of evaporation change if above activity is carried out on a rainy day. Justify your answer.
(CBSE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Evaporation will be faster under a fan. Since fan helps in the fast movement of the air, water will get more opportunity to evaporate under a fan than inside a cup board. In this case, the outside air will not come in contact with water.
(b) On a rainy day, there is humidity in air. As a result, evaporation of water will slow down.
Question 20:
A rubber band can change its shape on stretching; will you classify it as solid or not ? Justify your answer.
(CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Yes, it can be classified as a solid. It is an elastic solid which changes its shape on stretching and regains the same when the stretching force is removed.
Question 21:
When a solid melts, its temperature remains constant. Explain. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
The heat energy supplied once the solid starts melting is used up as latent heat of fusion. The melting point temperature of a solid gives an idea of the interparticular forces which bind the constituents in a solid. Thus, greater the melting point temperature, more will be the magnitude of intermolecular forces. For example,
Melting point temperature of sodium = 370 K
Melting point temperature of potassium = 336 K
This means that the attractive forces in atoms of sodium in the solid state of the metal are more than the forces that are present in the atoms of potassium also in the same state.
Question 22:
State one similarity and two differences between boiling and evaporation. (CBSE 2012, 2014, 2015)
Answer:
Similarity : In both evaporation and boiling, liquid changes to vapour state.
Differences :
- Evaporation takes place from the surface while boiling occurs throughout the liquid.
- Liquid can evaporate at all temperatures while boiling occurs only at a fixed temperature known as the boiling point temperature.
Question 23:
Draw a flow sheet diagram to illustrate interconversion of three states of matter. Name the process of each interconversion. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
It is because of the change in interparticle spaces and inter particle forces. If a solid is to be converted into liquid, the interparticle spaces have to be increased. Similarly, if a liquid is to change to the gas, these spaces have to be further increased.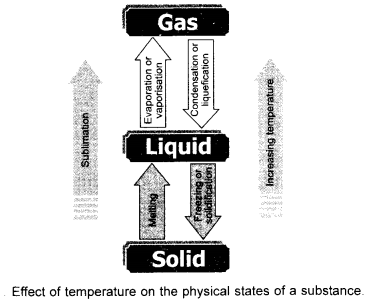
In other words, we can say that one state of a substance can be converted into the other by changing interparticle spaces.They actually change interparticle forces of attraction. Please note that the process can be reversed also under suitable conditions. This is known as interconversion of states of matter. The obvious question which strikes the minds of everybody is to how to bring about the change of state. There are two ways to achieve this.
By changing the temperature
By changing thé pressure.
Question 24:
- You want to wear your favourite shirt in a party, but the problem is that it is still wet after a wash. Mention three steps with reason that you would take to dry it faster ?
- It is a hot summer day. Priyanshi and Ali are wearing cotton and nylon clothes respectively. Who do you
think would be more comfortable and why ? (CBSE 2012, 2013, 2014, 2016)
Answer:
- Squeeze the shirt with force. By doing so, some of the moisture is removed.
- Spread the shirt on a stand. It provides greater surface area for evaporation.
- Iron the shirt. Increase in temperature helps in drying the shirt.
- Cotton clothes would be more comfortable than the nylon clothes since these are porous. Persipiration sticking to the skin can escape from the pores. Priyanshi would feel more comfortable.
Question 25:
Explain how three states of matter arise due to the variation in the characteristics of the particles.
(CBSE 2013)
Answer:
The three states of matter arise because of two characteristics
- Interparticle spaces : These are minimum in the solid state and maximum in the gaseous state.
- Interparticles forces of attraction : These are maximum in the solid state and minimum in the gaseous state.
Question 26:
List any two properties of liquids which are common to gases. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
- Both of them do not have any definite shape. They can take up the shape of the container in which these are kept,
- Both of them show the property of diffusion. However, gases diffuse faster.
Question 27:
How is heating of sugar different from heating of ammonium chloride ? Explain your answer. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Sugar melts upon heating whereas ammonium chloride sublimes upon heating without leaving behind any residue.
Question 28:
To which physical state of matter, do the following statements apply ? (CBSE 2013)
- incompressible, no fixed shape
- incompressible, high melting point
- compressible, no definite volume
- incompressible, highly fluid.
Answer:
- Liquid state
- Solid state
- Gaseous state
- Liquid state.
Question 29:
A drop of ink and a drop of honey are placed in watel in different beakers. Which of the two will spread faster ? Give reason for your answer. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Ink drop will spread faster as compared to honey. The density of honey is more than that of ink. Therefore, particles in ink diffuse faster as compared to the particles in honey.
Question 30:
Suppose you want to convert a gas into a liquid. Which two methods can you apply ? (CBSE 2013, 2016)
Answer:
- By increasing the pressure or by compressing the gas.
- By lowering the temperature or by cooling the gas.
Question 31:
Describe an activity to determine the melting point of ice with a diagram. (CBSE 2013, 2016)
Answer:
We know that the melting point of ice and the freezing point of water in pure states are both zero. This means that at this temperature, both are present. Upon heating, the temperature would actually not change but heat energy supplied would be absorbed by the ice as latent heat of fusion. This would result in the melting of ice.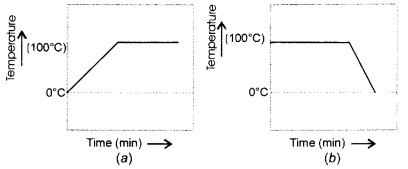
The temperature would remain zero degree till the whole of ice has melted. Further heating would increase the temperature of water till it starts boiling at 100°C. The curve (d) gives the correct representaton.
Question 32:
Explain why do wet clothes dry faster when we spread them out. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
By spreading wet clothes, the surface area available for evaporation increases. Therefore, wet clothes dry faster.
Question 33:
Describe an activity to show that particles of matter have spaces between them. (CBSE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
The important characteristics of the particulate nature of matter may be summed up as follows :
- Every matter is made up of particles.
- The particles constituting a matter are very small in size.
- The particles have empty or vacant spaces in them known as interparticle spaces.
- Particles are not stationary and are in a state of motion.
- Attractive forces are present in the particles of a substance. These are called interparticle forces.
- The particle motion increases with the rise in temperature.
Question 34:
How will you separate a mixture of naphthalene balls powder and common salt ? Draw a neat and labelled diagram to show the process. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
We have so far studied that upon heating, a solid initially changes to the liquid state and then to the gaseous state when the temperature is increased. The process or the change of state can be reversed when the temperature is decreased. However, there are some exceptions. Certain solids directly change to the gaseous state upon heating without passing through the liquid state. This is called sublimation. The substance obtained on cooling the vapours is known as sublimate. Sublimation may be defined as :
the change of solid directly into the gaseous state without passing through the liquid state upon heating.
Naphthalene balls, camphor, iodine, ammonium chloride are some common examples of the substances which undergo sublimation.
Question 35:
Define (a) Compressibility (b) Rigidity (c) Fluidity (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Compressibility: It is the property as a result of which the particles of any matter come closer on applying pressure.
(b) Rigidity: It is the capacity of the particles of a matter to resist a change in shape and size on applying stress.
(c) Fluidity: It is the property as a result of which particles of a matter have tendency to flow.
Question 36:
(a) Define the process of vaporisation.
(b) List four factors which affect the rate of evaporation. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
(a) vaporisation and may be defined as the amount of heat energy that is needed to convert one kg of a liquid at its boiling point temperature into its vapour state without any rise in temperature.
Latent heat of vaporisation of water is 226 kj kg-1. It is the amount of heat that is absorbed when one kilogram of water at its boiling point temperature (100°C) changes to vapour state without any further rise in temperature.
(b)
- Surface area available for evaporation
- Increase in temperature
- Decrease in humidity
- Increase in the speed of wind
Question 37:
State the physical state of water as the following temperatures.
(a) 373 K
(b) 300 K
(c) 200 K (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Gas or Vapours
(b) Liquid
(c) Ice.
Question 38:
Why does perspiration keep our body cool ? (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
Actually, we perspire a lot in the hot and humid weather. Since cooling is caused during evaporation, the body temperature gets lowered. We feel more comfortable. Now, cotton is of porous nature and is a good absorber of water coming out of the pores as sweat. The synthetic clothes are less porous and donot absorb sweat so quickly. As the sweat evaporates, it absorbs some energy from the body since the clothes are in contact with our skin. The temperature of the body gets lowered and we feel more comfortable. We feel less comfortable in nylon and terylene clothes during summer.
Question 39:
Tabulate three differences between boiling and evaporation. (CBSE 2015)
Answer: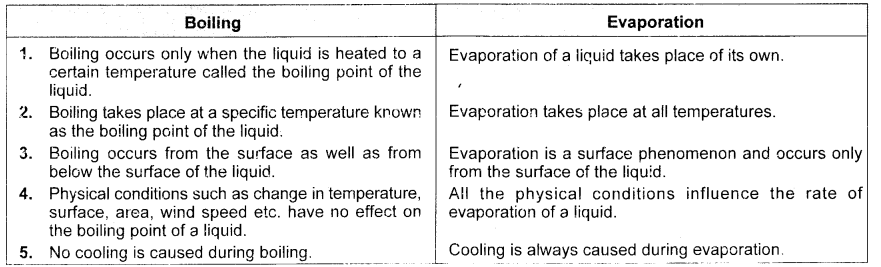
Question 40:
Give reasons for the following observations
- The smell of lighted incense stick spreads several metres away.
- A liquid has a fixed volume but not a fixed shape.
- Ice floats over water.
- A wooden table is called a solid at room temperature. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
- This happens because of diffusion. For example, the smell of food particularly of fish being cooked in the kitchen spreads in the lobby and even in different rooms because of diffusion.
- Liquids do not have fixed shapes and take up the shape of any container in which these are put. A liquid cannot be compressed on applying pressure. Actually, the interparticle forces in the liquids are so strong that the pressure which is applied is not in a position to overcome these. Liquids therefore keep their volume.
- Ice (solid state) floats over water (liquid state). Both are chemically same and are made from H2O molecules. Actually, the structure of ice is more porous* as compared to that of water. Therefore, for a given mass, the volume of ice is more than that of water and its density is comparitively less. As a result, ice floats over water.
- different containers. For example, blue crystals of copper sulphate have needle like shape which they retain whether kept in a beaker or in a china dish or placed on the palm of our hand.
Question 41:
(a) When common salt is added to water, will there be any change in volume ? Give reason.
(b) Write any one similarity between three states of matter. (CBSE 2015, 2016)
Answer:
(a) No, there will be no change in volume. The particles of common salt will occupy inter particle empty spaces present in the molecules of water. The salt will dissolve in water and there will not be any change in the level of the solution thus formed.
(b) All the three states of matter consist of particles which have specific mass.
Question 42:
Out of boiling and evaporation, which is a surface phenomenon ? Explain. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
Evaporation is a surface whereas boiling once started occurs throughout the liquid. In a liquid, the particles or molecules experience mutual forces of attraction. However, these are not stationary and have some kinetic energy at all temperatures. The particles of a liquid are also colliding with one another and exchanging energy during the collisions. Above the liquid surface, atmosphere or air is present which is a mixture of several gases. The particles of the liquid present on the surface have a tendency to come out from the surface so that they may acquire more freedom to move and become part of the atmosphere. This is also known as randomness. To overcome the interparticle forces of attraction, they need some energy which they take up from the rest of the particles or molecules of the liquid. As a result, their temperature gets lowered and cooling is caused.
Question 43:
Define boiling point. Write down the boiling point of water on Celcius scale and Kelvin scale. (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
The boiling point temperature of a liquid may be defined as :
the temperature at which a liquid starts boiling or the liquid state of a substance changes into gaseous/vapour state.
For example, the boiling point temperature of water is 100°C or 373 K. It is interesting to note that what we have noticed in the melting of a solid, also happens in the boiling of a liquid. It means that once the liquid starts boiling, its temperature does not change although it is still being heated. The explanation is also similar. As long as the liquid has not boiled, the heat energy which is supplied increases the kinetic energy of the particles (or H2O molecules) present in the liquid. As a result, the temperature rises. Once the liquid starts boiling, the heat energy is now being used to bring about a change in state from liquid to gas or vapours. It is known as latent heat of vaporisation and may be defined as :
the amount of heat energy that is needed to convert one kg of a liquid at its boiling point temperature into its vapour state without any rise in temperature.
Latent heat of vaporisation of water is 226 kj kg-1. It is the amount of heat that is absorbed when one kilogram of water at its boiling point temperature (100°C) changes to vapour state without any further rise in temperature.
Question 44:
Liquids and gases are commonly known as fluids. Compare their properties and show that they can flow easily.
(CBSE 2016)
Answer:
Unlike solids, the liquids have fluidity and not rigidity i.e., they have tendency to flow. This is due to lesser interparticle or intermolecular forces that are present in the liquid state as compared to the solid state. However, the liquids differ in their relative fluidity. For example, water flows at a faster rate than honey because in honey, the particles are heavier and also more closely packed.
Gases have maximum fluidity and least rigidity.
Since the interparticle spaces are the maximum in the gaseous state, the attractive forces are the least. As a result, the fluidity is very large while rigidity is negligible.
Question 45:
Tabulate the differences in the states of matter on the basis of the following characteristics :
- Rigidity
- Kinetic energy
- Density. (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
- Rigidity: We have seen that rigidity is maximum in the solid state and fluidity or particle motion is negligible. In the liquid state of a substance, both these characters are
different. The liquids are less rigid than the solids and the molecular motion is also comparatively more. - Kinetic energy: The kinetic energy is linked with movement of the particles from one place to the other. Since the constituents in the solid state are very closely packed, they have negligible kinetic energy. That is why solids do not flow.
- Density: Mass occupied by a solid per unit volume and is obtained by dividing the mass of a particular solid by the volume occupied by that mass of the solid.
The unit of density : kg/L or kg/dm³.










