Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 2
Question 1.
List the two conditions essential for using distillation as a method for separation of the components from a mixture. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
- The components of the mixture must be miscible with each other.
- In case, both the miscible components are liquids, they must differ in their boiling point by more than 25°C.
Question 2.
Water is a compound and not a mixture. Justify the statement giving two reasons. (CBSE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
- The two elements hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) are combined chemically to form water (H2O) which boils at a fixed temperature.
- The properties of water are altogether different from the constituting elements. For example, molecular hydrogen (H2) is combustible and molecular oxygen (O2) supports cumbustion. But water (H2O) extinguishes fire.
Question 3.
(a) Write one property of suspension.
(b) Identify solute and solvent in 80% solution of ethyl alcohol with water. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Suspension is of heterogeneous nature. The solid particles represent one phase while the liquid in which these are present, represents the other phase.
(b) Water present in smaller amount is solute. Ethyl alcohol present in excess is solvent.
Question 4.
(a) Classify Brass and Diamond as element and mixture.
(b) How is a chemical change different from a physical change ? (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Brass is a homogeneous mixture also called alloy. The constituents are Cu and Zn.
Diamond is an element. It is an allotropie form of carbon.
(b) In a chemical change, a new substance is formed as a result of chemical reaction. No new substance is formed in a physical change.
Question 5.
Why particles in a true solution cannot be seen with a naked eye ? (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Particle size in a true solution is less than 10-9 m or 1 nm. The particles are too small to scatter the beam of light and therefore, cannot be seen with naked eye.
Question 6.
(a) Identify the heterogeneous mixture from the following :
Air, soda water, soap solution, brass.
(b) Write two components of a colloidal solution. Give an example. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Soap solution is a heterogeneous mixture while the rest are of homogeneous nature.
(b) The two components of a colloidal solution are dispersed phase and dispersion medium. For example, a colloidal solution of starch in water (Starch acts as dispersed phase and water as the dispersion medium).
Question 7.
Distinguish between elements and compounds with one example of each. (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
An element cannot be broken into simpler or smaller constituents but a compound can be broken as a result chemical reaction or by passing electric current (electro-chemical reaction). For example, sodium (element), sodium chloride (compound).
Question 8.
Suggest a suitable separation technique for the following :
(a) Mercury and water.
(b) Coloured components from blue ink,
(c) Ammonium chloride and potassium chloride
(d) Mixture of alcohol and water.
(CBSE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
(a) The separation can be done by the use of separating funnel. Mercury forms the lower layer (heavier) and water the upper layer (lighter).
(b) The separation can be done with the help of chromatography.
(c) Process of sublimation can be used. Ammonium chloride collects as the sublimate while potassium
chloride remains in the dish. .
(d) Process of fractional distillation can be used. Alcohol (ethyl alcohol) with lower boiling point (78°C or 351 K) gets distilled leaving behind water with higher boiling point (100°C or 373 K) in the distilla¬tion flask.
Question 9.
A solution contains 60 g of sugar in 480 g of water. Calculate the concentration of solution in terms of mass by mass percentage of the solution. (CBSE 2010, 2012)
Answer: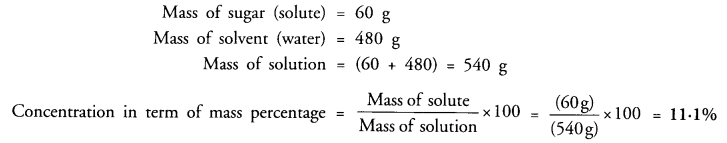
Question 10.
Identify the dispersed phase and dispersion medium in the following examples of colloids :
{a) Fog
(b) Cheese
(c) Coloured gem stone. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Fog : Liquid (water drops) acts as dispersed phase and gas (air) as the dispersion medium.
(b) Cheese : Solid (fat) acts as the dispersed phase and water (liquid) as the dispersion medium.
(c) Coloured gem stone : Solids act as the dispersed phase as well as the dispersion medium.
Question 11.
Differentiate between simple distillation and fractional distillation. (CBSE 2011, 2016)
Answer:
(a) In fractional distillation, a fractionating column is used while no such column is needed in simple distillation.
(b) Simple distillation can be used to separate two miscible liquids differing in their boiling points by more than 25°C. In case, the difference is less’than this, fractional distillation is used.
Question 12.
Define a solution. If 10 mL of H2SO4 are dissolved in 90 mL of water, calculate the concentration of solution. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
For the definition of solution,
Volume of H2SO4 (solute) = 10 mL
Volume of water (solvent) = 90 mL
Volume of solution = (90 +10) mL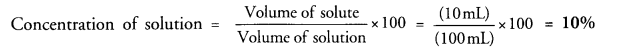
Question 13.
- Why is crystallisation technique better than evaporation ?
- Write any two physical properties each of metals and non-metals.
- Name the technique used to separate butter from curd. (CBSE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
- Both these techniques are used to separate the solid substances from their solutions. But crystallisation is considered better because during evaporation certain solids may decompose or some of them like sugar get charred when the solution is evaporated completely to dryness. As a result of crystallisation, even the shapes of the crystals donot change.
- Metals have a shining surface known as lustre.
- Metals are malleable and ductile.
- Non-metals are mostly poor conductors of electricity.
- Non-metals are generally soft.
- Butter can be separated from curd by the process of centrifugation. This is usually done by churning
which is very common as well as convenient.
Question 14.
Define distillation. What type of mixtures can be separated by distillation ? Draw a labelled diagram of the apparatus used for fractional distillation. (CBSE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
For the definition of distillation, The process of distillation, also called simple distillation can be used :
- to separate two miscible liquids which differ in their boiling point temperature by 25°C or more.
- to purify an impure liquid containing soluble non-volatile impurities.
For the labelled diagram of the apparatus used for fractional distillation,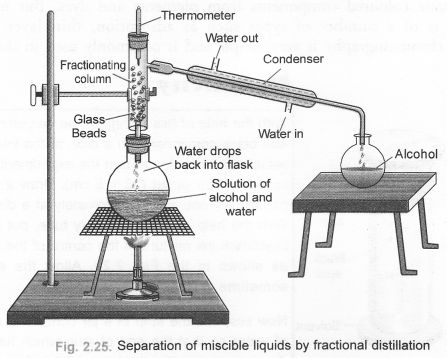
Question 15.
(a) 110 g of a solute are present in 550 g of solution. Calculate the concentration of solution.
(b) Give any three points of difference between true solution, colloidal solution and suspension.
(CBSE 2011)
Answer: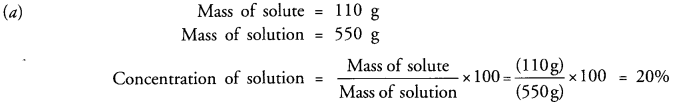
(b)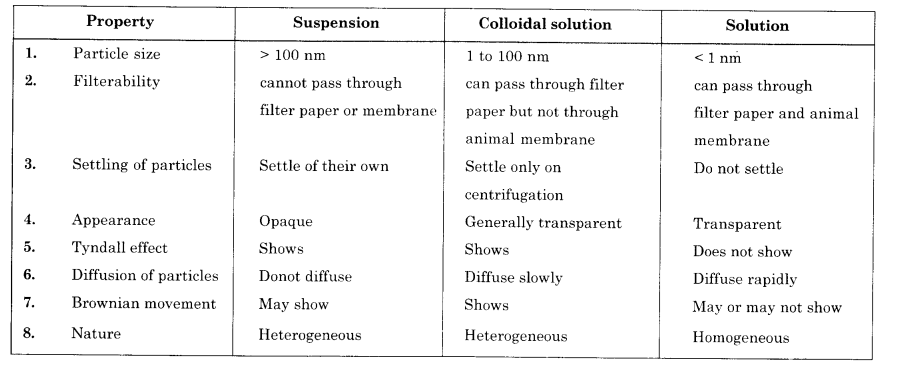
Question 16.
State one instance where water undergoes a physical change and one in which it undergoes a chemical change.
(CBSE 2010)
Answer:
Physical change : Evaporation of water or freezing of water Chemical change : Electrolysis of water.
Question 17.
You are given a mixture of sand, water and mustard oil. How will you separate the components of this mixture ? Explain with the help of different separation methods involved in it. (CBSE 2010, 2011, 2016)
Answer:
The separation of the components from this heterogeneous mixture can be done in the following steps. Step I. Filter the mixture through a glass funnel.
Water and mustard will be collected as filtrate while sand particles will remain on the filter paper as residue.
Step II. Now transfer the mixture of water and mustard oil to a separating funnel and proceed as discussed in section. Water will form the lower layer in the funnel while mustard oil the upper layer. Separate the two layers.
Question 18.
Sudha tested the solubility of four salts X, Y, Z and T at different temperatures and collected the following data. (Solubility refers to the amount in grams dissolved in 100 g of water to give a saturated solution.)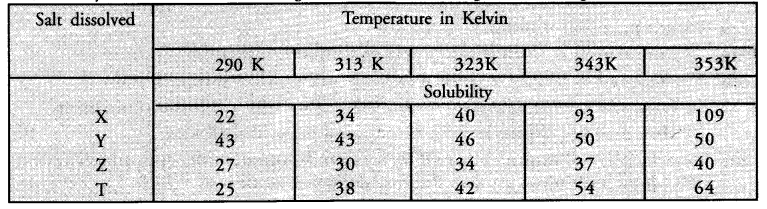
Answer the following questions from the table
(i) Which salt has the highest and lowest solubility at 323 K ?
(ii) A student prepared a saturated solution of X at 323 K and then added 25 g water to it. What mass of X must be added to again make the solution saturated ?
(iii)The solubility of which salt is least affected by increase in temperature ?
(iv) What mass of ‘T’ would be required to make saturated solution in 200 g of water at 290 K ?
(CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Question 19.
State which of the following solutions exhibit Tyndall effect :
Starch solution, Sodium chloride solution, Tincture of iodine, Air.
Answer:
- Tyndall effect is shown both by starch solution and air which are heterogeneous mixtures and have the capacity to scatter beam of light as it passes through them.
- Sodium chloride solution and tincture of iodine (iodine crystals dissolved in ethyl alcohol) are both homogeneous in nature and donot exhibit any Tyndall effect.
Question 20.
Identify colloids from the following :
Copper sulphate solution, milk, smoke, muddy water, butter, sugar solution, face cream, lemonade.
(CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Colloids : milk, smoke, muddy water, butter, face cream, lemonade.
Question 21.
List any three differences between true solution and suspension. (CBSE 2012)
Answer: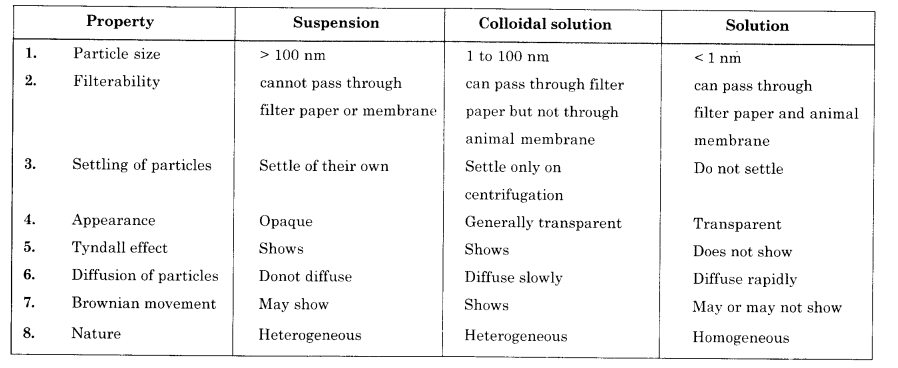
Question 22.
12 mL of dettol is added to a beaker containing 500 mL of water and is stirred. State four observations that you make. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
When dettol is added to a beaker containing of water, the following observations are made.
- An emulsion is formed which is of colloidal nature.
- The colour of emulsion is milky.
- It gives characteristic smell of dettol.
- The solution can pass through a filter paper.
Question 23.
Properties of a compound are different from its constituents, while a mixture shows the properties of its constituent elements. Justify this statement taking the example of iron and sulphur. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Take a small amount of the material from dish [A] in a glass tube and add a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid to it. A colourless and odourless gas will evolve accompanied by brisk effervescence. This is hydrogen gas which can be confirmed by performing certain tests.
In a similar manner, add a few drops of the same acid to the material taken from the dish B. Immediately a gas with the smell similar to rotten eggs will evolve. It is hydrogen sulphide gas.
Conclusion: From the observations listed above, we conclude that in the china dish [A], both iron filings and powdered sulphur are in the form of a mixture. In the dish [B], a chemical reaction has resulted upon heating and the black mass of iron sulphide is formed. It is a compound.
Iron + Sulphur ———- > Iron sulphide
Question 24.
Give one example in which physical and chemical changes take place. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
It is illustrated by burning of candle. One such example is the burning of candle. The wax present in the candle changes to liquid state. This means that the change is of physical nature. At the same time, the constituents carbon and hydrogen present in wax react with oxygen of air to form new substances. This means that a chemical reaction or change is also taking place.
Question 25.
(a) Enumerate any two differences between simple distillation and fractional distillation.
(b) Draw a labelled diagram showing the process of fractional distillation. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
- Simple distillation can be used if the liquids to be separated differ in their boiling points by more than 25°C. If the difference is less, than fractional distillation can be used.
- A fractionating column is needed for fractional distillation but not for simple distillation.
(b) For process of fractional distillation,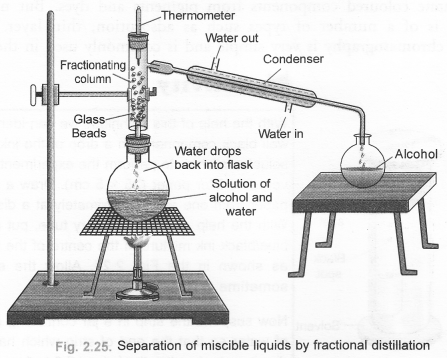
Question 26.
On dissolving chalk powder in water, a suspension is obtained. Give any four reasons to support the fact that mixture so obtained is a suspension only. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
It is supported by the following reasons
- White particles of chalk powder can be seen with naked eye.
- The particles can be separated by ordinary filter paper.
- Upon shaking, a white turbidity reappears in solution.
- Light cannot pass through the suspension which shows that it is of opaque nature.
Question 27.
(a) Crystallization is a better technique than evaporation. Give one reason to justify the statement.
(b) Draw a labelled diagram to show the process of separation of two immiscible liquids. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Crystallisation technique is always better than evaporation due to the following reasons.
- Some solids may decompose and some substances like sugar may get charred during direct heating.
- Some minute impurities of particles may still be associated in the solution obtained upon filtration. They will be present in the solid residue left after evaporation. In crystallisation, the crystals obtained are always pure.
- Direct heating or evaporation does not give crystals. Only a solid residue is left in the dish.
(b) The separation can be done by the use of separating funnel.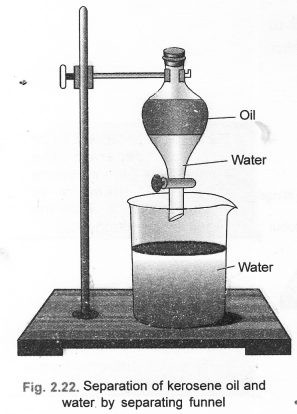
Question 28.
When a solution is said to be saturated ? How can you change a saturated solution to an unsaturated solution without adding any more solvent to it ? Explain in brief. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
A solution is said to be saturated if it has the maximum amount of the solute dissolved in a given amount of the solvent at a given temperature.
Saturated solution can also be made unsaturated by increasing the temperature provided the process of dissolution of the solid solute is of endothermic nature i.e., it is accompanied by the absorption of heart.
Question 29.
Name the type of colloids in each of the following giving an example of each.
Answer:
Question 30.
How are colloids different from suspensions ? . (CBSE 2013, 2016)
Answer:
- In a suspension the particles settle as precipitate when it is allowed to remain undisturbed for sometime.
- Colloidal solutions are of heterogeneous nature. They consist of two phases known as dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
Question 31.
Identify the colloids from the following :
Soda water, milk, sponge, clouds, mixture of alcohol and water, jelly. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Colloids : Soda water, milk, sponge, clouds, jelly.
Question 32.
How will you separate a mixture of common salt, camphor and iron filings ? Describe the process.
(CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Iron filings are first separated with the help of a magnet. Camphor is separated from the remaining mixture with the help of sublimation process leaving behind common salt.
- In a colloidal solution, the particle size is such (1 nm to 100 nm), that these particles scatter the light rays as they fall on them. Because of scattering, the path of the light as well as the particles become visible. But in a true solution, the particle size is so small (less than 1 nm) that these particles are not in a position to scatter the light. Therefore, true solution does not show any Tyndall effect.
- In dirty clothes, the dust particles are sticking on the oil drops present. Simple water cannot remove these oil drops from the clothes because water and oil as such do not form a stable emulsion. Soap plays the role of emulsifier and helps in forming a stable emulsion between the two. In other words, it helps in mixing oil and water. This means that soap helps in removing these oil drops along with the dirt sticking to them. The dirty clothes get washed by soap solution.
Question 33.
Give an example each for a mixture having following characteristics :
- Two or more coloured constituents soluble in a solvent.
- Two immiscible liquids.
- One of the components changes directly to the gaseous state.
Suggest a suitable method to separate the components of these mixtures. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
- Sulphur (a yellow solid) and iodine (a violet crystalline solid) are both soluble in carbon disulphide (CS2) solvent. Separation can be done by sublimation. Iodine sublimes on heating while sulphur does not.
- Turpentine oil and water. Separation can be done with a separating funnel.
- Ammonium chloride and common salt. Ammonium chloride directly changes to vapour state (sublimes).
Question 34.
Give an example for each of following :
- Solid-liquid homogeneous mixture
- Gas-Gas homogeneous mixture
- Liquid—Liquid heterogeneous mixture. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
- Mixture of sodium chloride in water.
- Air: It is a homogeneous mixture of number of gases.
- Emulsion of oil and water.
Question 35.
List any two properties of metals which make them suitable to be used as :
- Utensils for cooking food.
- Wires for electrical connections. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
- Metals are good conductors of heat.
- Metals are good conductors of electricity and also ductile in nature.
Question 36.
To make a saturated solution, 36 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of water at 293 K. Find the concentration in terms of mass of solution at this temperature. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Mass of solution = Mass of solute + Mass of solvent = (36 + 100) = 136 g.
Question 37.
Which separation techniques you will apply for the separation of the following mixtures ?
- Oil from warter
- Camphor from sand
- Sodium chloride from its solution in water
- Cream from milk
- Metal pieces from engine oil of a car.
Answer:
- By the use of a separating funnel.
- With the help of sublimation technique.
- By crystallisation technique.
- By the use of a centrifugal machine.
- By the use of filtration technique.
Question 38.
‘Water is considered as a compound of hydrogen and oxygen and not a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen.’ Comment on it.
Differentiate between a compound and a mixture (any three points). (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
The properties of water are altogether different from those of the constituting gases. For example, water is a liquid at room temperature whereas the constituents are in the gaseous state. Water can extinguish fire whereas hydrogen is combustible in nature, oxygen supports combustion.
Question 39.
How will you separate a mixture containing kerosene and petrol (difference in their boiling point is less than 25 K) which are miscible with each other ? Explain. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
Both are miscible liquids. Since the difference in the boiling points is less than 25 K, the separation can be done with the help of fractional distillation technique. Petrol with less boiling point distils first leaving behind kerosene in the distillation from flask. However, it is very difficult to apply this technique since both are highly flammable liquids and a great deal of precaution is needed.
Question 40.
List two differences between a pure substance and a mixture. Give an example of each. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
- A pure substance is an element or compound in completely pure state while mixture may contain two or more elements/compounds.
- Constituents from a mixture can be separated while pure substance remains as a single substance. Example : Copper (pure substance); Air (Mixture).
Question 41.
Classify the following as compund and mixture. Saline water, water, air, carbon dioxide, hydrogen chloride, milk. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
Compound : Water, carbon dioxide, hydrogen chloride.
Mixture : Saline water, air, milk.
Question 42.
Explain the terms dilute solution, concentrated solution and saturated solution. How would you determine the solubility of a solution ? What is the effect of change of temperature on the solubility ? (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
For dilute and concentrated solutions: We have read that a binary solution has two components or constituents. These are solute and solvent. The relative amounts of the solute and solvent in the solution either by mass or by volume, represent the concentration solution. Expressing the Concentration of a Solution.
The concentration of a solution is expressed as the amount of the solute present in a given amount of the solvent or solution. It is normally expressed as mass by mass percent or as volume by volume percent.
For saturated solutions: A solution becomes saturated if the solute starts separating at the bottom of the container in which the solution is being prepared at a given temperature. A saturated solution generally becomes unsaturated upon heating
For the determination of the solubility of a solution: The solubility of a solute in a solution is always expressed with respect to the saturated solution. It may be defined as : The maximum amount of the solute which can be dissolved in 100 g (0-1 kg) of the solvent to form a saturated solution at a given temperature.
For the effect of change in temperature on the solubility: The temperature at which the process of dissolution is carried is always mentioned. This means that the solubilities of salts in solvents (generally water) are influenced by the change in temperature. Actually, the effect of temperature depends upon the heat energy changes which accompany the process.
Question 43.
Why is crystallisation better than evaporation for the separation of mixtures ? (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
- Common salt and water. Since common salt (sodium chloride) is soluble in water, it can be separated by crystallisation. The process of distillation can also be used because sodium chloride is non-volatile and water is volatile in nature.
- Iodine and sand. Sublimation process can be used. Iodine will sublime on heating while sand will remain unaffected.
- Kerosene and water. The liquids are not miscible with each other. Separation can be done by using a separating funnel.
Question 44.
Sugar and sulphur. The mixture is dissolved in carbon disulphide in a beaker by stirring with a glass rod. Sulphur dissolves while sugar remains as such. On filtering, sugar separates as the residue. The filtrate upon concentration and cooling gives crystals of sulphur.
Give one example each of a mixture which shows the following characteristics.
- A mixture of two volatile component.
- A mixture of two volatile components with a boiling point difference less than 25 K.
- A mixture of a volatile and a non-volatile component. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
- Iodine and camphor
- Acetone (b.p. = 319 K) and ethyl alcohol (b.p. = 341 K)
- Naphthalene and sodium chloride.
Question 45.
Differentiate between an element and a compound. Categorize the following substances into elements and compounds.
Sodium chloride, iodine, water, 24 carat gold, oxygen gas, carbon. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
For distinction between element and compound,
Elements : Iodine, 24 carat gold, carbon.
Compounds : Sodium chloride, water, oxygen gas.
Question 46.
Air is considered to be a mixture and not a compound ? Explain. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
Air is a homogeneous mixture of different gases which can be separated by suitable methods. Therefore, it is a mixture and not a compound.
Question 47.
Observe the apparatus shown and answer the following questions.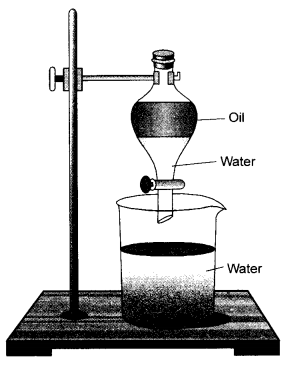
- Identify the apparatus
- Design an activity to use this apparatus to separate the mixture of mustard oil and water.
- Write the principle involved in this process. (CBSE 2015, 2016)
Answer:
- The apparatus is known as a separating funnel.
- For the details of the apparatus & activity.
- Two immiscible liquids can be separated if in case they differ in their densities. A separating funnel can be used to separate the components of an immiscible liquid mixture.
Question 48.
Compare suspension and colloidal solution on the basis of
- type of mixture
- particle size
- scattering of light
- stability. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
- Both are heterogeneous mixture.
- In colloidal solution, particle size ranges between 10-9 m to 10-7 m whereas in suspension, the particle size is more than 10-7m.
- Colloidal solution has the capacity to scatter the path of light when made to pass through it whereas a suspension is unable to do so.
- A suspension is more stable than a colloidal solution.
Question 49.
A solution contains 50 g of sugar in 450 g of water. Calculate the concentration in terms of mass by mass percentage of the solution. (CBSE 2015)
Answer: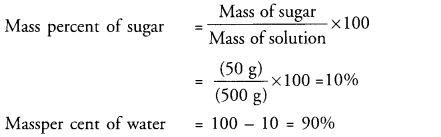
Question 50.
What is ‘Tyndall effect’ ? Name two mixtures which show this effect. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
For Tyndall effect, The scattering of the beam of light by the dispersed phase particles in a colloidal solution as it passes through it, is known as Tyndall effect.
- A colloidal solution of dust particles suspended in air.
- A colloidal solution of starch in water.
Question 51.
What is chromatography ? Write its two applications. (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
In Greek, the word ‘Kroma’ means colour and the word chromatography implies ‘writing, in colour’. Actually, this technique was initially used to separate coloured components from pigments and dyes. But now it has wide range of applications. Chromatography is of a number of types such as adsorption, thin layer, paper and gas chromatography etc. However, the paper chromatography is very simple and is commonly used in the laboratory.
Question 52.
(a) Compare metals and non-metals based on their physical properties (any four).
(b) What are metalloids ? Give two examples.
(c) Identify metals from the following :
boron, sodium, mercury, carbon. (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
(a)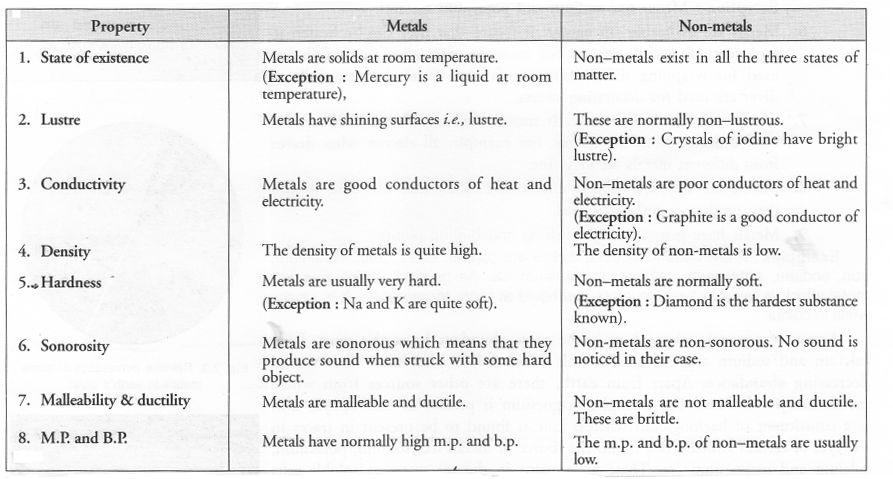
(b) Semi-Metals or Metalloids: There are a few elements which possess the characteristics of both metals and non-metals. These are actually border-line elements and are known as semi-metals. Semi-metals are also called metalloids. A few common examples are : Silicon, Arsenic, Antimony and Bismuth.
(c) Sodium and mercury are metals.
Question 53.
List six physical properties of metals. Name two metals. Name a metal which is liquid at room temperature.
(CBSE 2016)
Answer: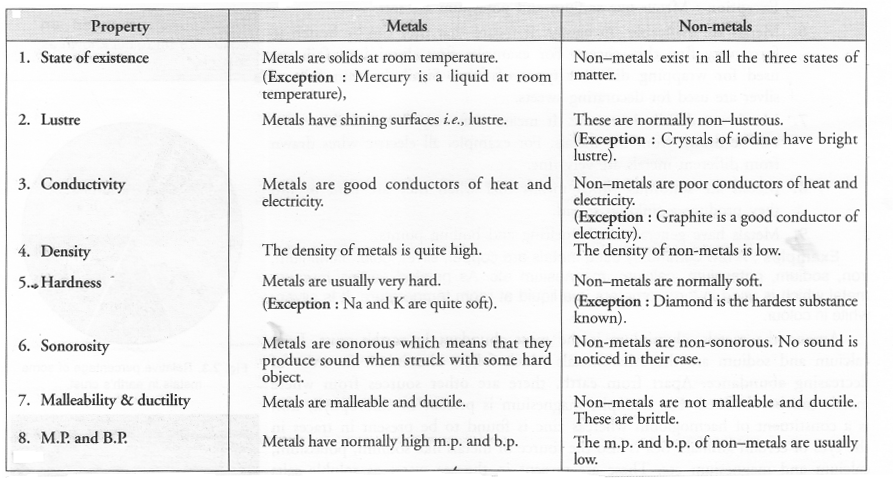
Question 54.
Give two differences between pure substances and mixtures. Give one example of each. (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
- A pure substance is always a single substance (element or compound). A mixture has two or more constituents.
- A pure substance has always sharp melting or boiling point. A mixture does not have sharp melting or boiling point.
Examples : Copper sulphate (Pure substance), Air (Mixture)










