Important Questions of Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 Science Chapter 5
Question 1.
State Mendeleev s Periodic law.
Answer:
Medeleev’s periodic law states that the properties of elements are periodic function of their atomic masses.
Question 2.
Why did Mendeleev leave some gaps in the Periodic table?
Answer:
Mendeleev left some gaps in the periodic table for yet to be discovered elements. Mendeleev predicted the properties of these elements on the basic of their positions. For example, he predicted the properties of gallium (eka-aluminium) and germanium (eka-silicon) which were unknown at that time.
Question 3.
If the letter ‘R’ was used to represent any of the elements in the group, then the hydride and oxide of carbon would respectively be represented as
(a) RH4, RO
(b) PH4, RO2
(c) RH2, RO2
(d) RH2, RO
Answer:
(b) CH4 is written for hydride and CO2 is written for oxide of carbon.
Question 4.
Isotopes are
(a) atoms of an element with similar chemical properties but different atomic masses
(b) atoms of different elements with similar chemical properties but different atomic masses
(c) atoms of an element with different chemical properties but same atomic masses
(d) atoms of different elements with different chemical properties but same atomic masses. (2020)
Answer:
(a) Isotopes have same atomic number, hence similar chemical properties and different atomic masses.
Question 5.
How many metals are present in second period of periodic table? (2020)
Answer:
Two metals (lithium and beryllium) are present in second period of periodic table.
Question 6.
On the basis of electronic configuration of
(a) group 15 period 2
(b) group 13 period 2
(c) group 9 period 5
(d) group 13 period 5. (2020)
Answer:
(b) For element X of atomic number 5, the electronic configuration is 2,3. So, it has 3 valence electrons and hence it belongs to group 13. As five electrons are filled in two shells, so it belongs to 2nd period.
Question 7.
An element ‘X’ with atomic number 11 forms a compound with element ‘Y’ with atomic number 8. The formula of the compound formed is
(a) XY
(b) X2Y
(c) XY2
(d) X2Y3 (2020)
Answer:
(b): The electronic configuration of X is 2, 8, 1. Hence, it belongs to group 1. Its valency is 1.
The electronic configuration of Y is 2, 6. Hence, it belongs to group 16. Its valency is 2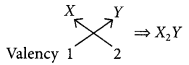
Question 8.
Define electropositivity. (2020)
Answer:
Electropositivity is the measure of the ability of elements (mainly metals) to donate electrons to form positive ions.
Question 9.
The atomic radii of first group elements are given below:
| Group-I element | Atomic Radii (pm) |
| Na | 86 |
| K | 231 |
| Rb | 244 |
| Cs | 282 |
State the reason behind the observed trend in the above elements. (2020)
Answer:
On moving down the group, the new shells are being added. This increase the distance between outermost shell and nucleus, hence the atomic radii of elements increase gradually down the group in spite of the increase in nuclear change.
Question 10.
An element ‘X’ is forming an acidic oxide. Its position in modern periodic table will be
(a) group 1 and period 3
(b) group 2 and period 3
(c) group 13 and period 3
(d) group 16 and period 3. (2020)
Answer:
(d) : As the element X forms an acidic oxide, hence ‘X is a non-metal. Hence, X is sulphur.
Question 11.
Consider the following statements about an element ‘X with number of protons 13.
(A) It forms amphoteric oxide.
(B) Its valency is three.
(C) The formula of its chloride is XCl3.
The correct statements is/are
(a) only (A)
(b) only (B)
(c) (A) and (C)
(d) (A), (B) and (C). (2020)
Answer:
(d) The number of protons in X is 13. Hence, its atomic number is 13. The electronic configuration of X is 2, 8, 3. Hence, it is a group 13 element i.e., X is aluminium. Aluminium forms amphoteric oxide, its valency is 3 and formula of aluminium chloride is AlCl3.
Question 12.
Write the number of valence electrons present in a nitrogen atom (
Answer:
The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. Its electronic configuration is 2, 5. The number of valence electrons in it is five.
Question 13.
Write the number of vertical columns in the Modern Periodic Table. What are these columns called? (Delhi 2014, 2013)
Answer:
There are 18 vertical columns in the Modern periodic table which are called groups.
Question 14.
Write the number of horizontal rows in the Modern Periodic Table. What are these rows called? (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
There are seven horizontal rows of elements in the Modern periodic table which are known as periods.
Question 15.
Write any one difference in the electronic configurations of group 1 and group 2 elements. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Group 1 elements have one electron in their outermost shell while group 2 elements have two electrons in their outermost shell.
Question 16.
List any two properties of the elements belonging to the first group of the Modern Periodic Tablet (AI 2014)
Answer:
Two properties of the elements belonging to the first group:
(i) As the elements belong to group 1, so they have one electron in their outermost shell hence, valency of these elements is one.
(ii) Alkali metals (group 1 elements) are electropositive in nature.
Question 17.
Write the atomic numbers of two elements ‘X’ and ‘Y’ having electronic configurations 2, 8, 2 and 2, 8, 6 respectively. (AI 2014)
Answer:
Electronic configuration of X = 2, 8, 2
∴ Atomic number = 2+ 8 + 2 = 12 Similarly,
Electronic configuration of Y = 2, 8, 6
∴ Atomic number = 2 + 8 + 6 = 16
Question 18.
The atomic numbers of three elements A, B and C are 12, 18 and 20 respectively. State giving reason, which two elements will show similar properties. (AI 2014)
Answer:
Atomic number of A = 12
∴ Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 2
Similarly, for B(18) = 2, 8, 8
for C(20) = 2, 8, 8, 2
As elements A and C contain two valence electrons in their outermost shell (group-2) they will show similar properties.
Question 19.
State the Modern periodic law of classification of elements. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
Modern periodic law states that the physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic numbers.
Question 20.
Out of the three elements P, Q and R having atomic numbers 11, 17 and 19 respectively, which two elements will show similar properties and why? (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
Atomic number of P = 11 Electronic configuration of P = 2, 8,1 Electronic configuration of Q(17) = 2, 8, 7 and for R(19) = 2, 8, 8, 1
Thus, from electronic configurations of P and R, it is observed that they belong to group 1 as both have one valence electron and have valency equal to 1. Thus, P and R will have similar properties.
Question 21.
Write the formula used to determine the maximum number of electrons which a shell in an atom can accommodate. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in a shell, is given by the formula 2n², where ‘n is the number of the shell.
Question 22.
How it can be proved that the basic structure of the Modern Periodic Table is based on the electronic configuration of atoms of different elements? (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Electronic configuration of an element decides its position in Modern periodic table.
Lets take an example of sodium (Na).
Atomic number of sodium = 11
Thus, electronic configuration of Na = 2, 8, 1 As Na contains 1 electron in its outermost shell, it belongs to group 1. Sodium contains 3 shells so, it belongs to period number 3.
Thus, we can conclude that
Group number = Number of valence electrons
(When valence electrons are 1 and 2) and group number = 10 + valence electrons
(When valence electrons are 3 and above) Period number = Number of shells in which electrons are filled.
Question 23.
The electronic configuration of an element is 2, 8, 4. State its
(a) group and period in the Modern Periodic Table.
(b) name and write its one physical property. (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
(a) The element belongs to group 14 and 3rd period of the Modern Periodic Table.
(b) The element is silicon. It is non-lustrous.
Question 24.
An element X has atomic number 13 :
(a) Write its electronic configuration.
(b) State the group to which ‘X’ belongs?
(c) Is ‘X a metal or a non-metal?
(d) Write the formula of its bromide. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
X has atomic number = 13
(a) Electronic configuration of X = 2, 8, 3
(b) As X contains 3 valence electrons in its outermost shell, it belongs to group 13.
(c) X is a metal as it contains 3 valence electrons which can be lost easily.
(d) Formula of X with bromine will be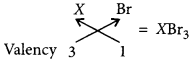
Question 25.
How can the valency of an element be determined if its electronic configuration is known? What will be the valency of an element of atomic number 9(nine)? (Delhi 2012, 2011)
Answer:
Valency of an element is determined by the number of electrons present in its outermost shell. For elements having outermost electrons 1 to 4, valencies are equivalent to their respective valence electrons.
For elements having outermost electrons 5 to 8, valency is calculated as;
Valency = 8 – (Number of valence electrons)
For element having atomic number = 9
Electronic configuration = 2, 7
Valency = 8 – 7 = 1
Question 26.
Choose from the following :
6C, 8O, 10Ne, 11Na, 14Si
(i) Elements that should be in the same period.
(ii) Elements that should be in the same group.
State reason for your selection in each case. (AI 2012)
Answer:
The electronic configurations of the given elements are:
6C = 2, 4
8O = 2, 6
10Ne = 2, 8
11Na = 2, 8,1
14Si = 2, 8, 4
(i) 6C, 8O, 10Ne, all contain two shells hence, they belong to same period i.e., second period.
11Na, 14Si both contain three shells hence, they belong to third period.
(6C, 8O, 10Ne) ⇒ period number 2
(11Na, 14Si) ⇒ period number 3
(ii) 6C and 14Si belong to the same group as they both contain 4 electrons in their outermost shell. Thus, 6C and 14Si belong to group 14.
Question 27.
An element ‘X’ belongs to 3rd period and group 17 of the periodic table. State its
(i) electronic configuration, (ii) valency Justify your answer with reason. (AI 2012)
Answer:
As element X belongs to group 17, it will have 7 electrons in its outermost shell. Moreover, X belongs to period number 3 so, it will have 3 shells.
(i) Electronic configuration of X = 2, 8, 7
(ii) Valency of element X
= 8 – (Number of valence electrons) = 8 – 7 = 1
Question 28.
Choose from the following :
4Be, 9F, 19K, 20Ca
(i) The element having one electron in the outermost shell.
(ii) Two elements of the same group. (Foreign 2012)
Answer:
The electronic configurations of the given elements are:
4Be = 2, 2
9F = 2, 7
19K = 2, 8, 8,1
20Ca = 2, 8, 8, 2
(i) Potassium (K) has one electron in its outermost shell.
(ii) Be and Ca have two electrons in their outermost shells hence, they belong to same group.
Question 29.
An element has atomic number 13.
(a) What is the group and period number to which this element belongs?
(b) Is this element a metal or a non-metal? Justify your answer. (Foreign 2012)
Answer:
Atomic number of element = 13
Thus, its electronic configuration = 2, 8, 3
(a) From the electronic configuration, it can be easily seen that there are 3 electrons in the outermost shell which indicates that it belongs to group number 10 + 3 = 13.
Moreover, the element has 3 shells in which electrons are filled thus, it belongs to period number 3.
(b) As the element contains 3 valence electrons which can be easily lost thus, it is a metal.
Question 30.
How does the electronic configuration of an
atom of an element relate to its position in the Modern Periodic Table? Explain with one example. (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
Refer to answer 22.
Question 31.
How does the valency of elements vary (i) in going down a group, and (ii) in going from left to right in a period of the periodic table? (AI 2011)
Answer:
(i) When we go down the group the valency of elements remains same.
(ii) When we move along the period from left to right, the valency of elements first increases and then decreases.
Question 32.
In the Modern Periodic Table, the element calcium (atomic number = 20) is surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 12, 19, 21 and 38. Which of these elements has physical and chemical properties resembling those of calcium and why? (AI 2011)
Answer:
From the given data, the electronic configuration of different elements can be written as:
Calcium (20) = 2, 8, 8, 2
Element with atomic number 12 = 2, 8, 2
Element with atomic number 19 = 2, 8, 8,1
Element with atomic number 21 = 2, 8, 8, 3
Element with atomic number 38 = 2, 8,18, 8, 2
It can be easily seen that elements with atomic numbers 12 and 38 have two electrons in their outermost shell thus, they belong to same group as that of calcium. So, they will show the physical and chemical properties resembling those of calcium.
Question 33.
In the periodic table, how does the tendency of atoms to loose electrons change on going from
(i) left to right across a period?
(ii) top to bottom in a group? (Foreign 2011)
Answer:
(i) Tendency of atoms to loose electrons decreases from left to right in a period due to increase in effective nuclear charge.
(ii) Tendency of atoms to loose electrons increases down the group due to increase in atomic radii.
Question 34.
What is meant by periodicity of properties of elements? Why are the properties of elements placed in the same group of the periodic table similar? (Foreign 2011)
Answer:
When elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic numbers, elements with similar chemical properties are repeated at definite intervals. Ibis is known as periodicity of properties of elements.
Elements placed in the same group of the periodic table have similar properties because they have same number of outermost electrons and hence, show same valency. Thus, they all will form similar type of compounds.
Question 35.
The position of three elements A, B and C in the modern periodic table is as follows :
(a) Write formula of compound formed between:
(i) B and A (ii) B and C
(b) Is any of the three elements a metal? Give reason to justify your answer. (2020)
Answer:
(a) (i) B belongs to group 1, hence its valency is 1.
A belongs to group 17, hence its valency is also 1.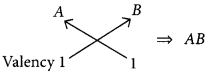
(ii) C belongs to group 16, hence, its valency is 2.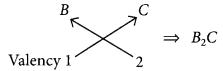
(b) As B belongs to group 1, it contains one valence electron which can be easily lost. Hence, B is a metal.
Question 36.
Three elements X, Y and Z have atomic numbers 7, 8 and 9 respectively.
(a) Arrange them in the decreasing order of their atomic radii.
(b) Which of the three is most electronegative? Why?
(c) Write the formula of compound formed between
(i) X and Y (ii) X and Z (2020)
Answer:
For element X of atomic number 7, the electronic configuration is 2, 5 so it has 5 valence electrons and hence, it belongs to group 15. As seven electrons are filled in two shells so, it belongs to 2nd period.
Similarly, for 7(8), electronic configuration = 2, 6
Period number = 2, Group number = 16 and for Z(9) = 2, 7
Period number = 2, Group number = 17
(a) As size of the atoms decreases on moving from left to right in a period so, the order of atomic radii will be : X > Y > Z.
(b) As electronegativity increases in moving left to right in a period so, the most electronegative element will be Z.
(c) (i) Formula of the compound when X combines with Y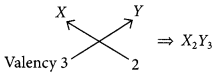
(ii) Formula of the compound when X combines with Z: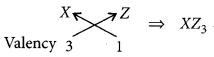
Question 37.
Based on the group valency of elements write the molecular formula of the following compounds giving justification for each:
(i) Oxide of first group elements
(ii) Halide of the elements of group thirteen, and
(iii) Compound formed when an element, A of group 2 combines with an element, B of group seventeen. (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
(i) Oxides of group 1 elements :
Let the element be A.
As A belongs to group 1 of the periodic table, it will have valency = 1.
So, chemical formula of its oxide will be A O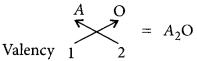
(ii) Halides of the element of group-13 :
Let the element be D.
As D belongs to group 13, it will have valency = 3 Halide X has the valency = 1
So, chemical formula will be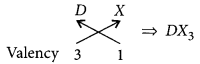
(iii) Valency of A = 2
Valency of B = 1
Chemical formula of the compound will be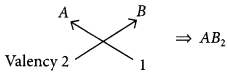
Question 38.
Write the names given to the vertical columns and horizontal rows in the Modern Periodic Table. How does the metallic character of elements vary on moving down a vertical column? How does the size of atomic radius vary on moving left to right in a horizontal row? Give reason in support of your answer in the above two cases. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
In Modern periodic table, there are 18 vertical columns called groups and 7 horizontal rows called periods.
The elements which have a greater tendency to loose electrons are more metallic thus, the metallic character of elements increases down the group as their tendency to loose electrons increases. Atomic radius decreases as we move from left to right in a horizontal row. At each successive element, the electron enters to the same shell due to which there is increase in nuclear charge and the electrons are pulled with greater attractive force. Hence, the atomic size decreases.
Question 39.
An element P (atomic number 20) reacts with an element Q (atomic number 17) to form a compound. Answer the following question giving reason:
Write the position of P and Q in the Modern Periodic Table and the molecular formula of the compound formed when P reacts with Q. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Atomic number of P = 20
∴ Electronic configuration of P = 2, 8, 8, 2
Atomic number of Q = 17
∴ Electronic configuration of Q = 2, 8, 7 As P contains 4 shells, it belongs to 4th period and due to presence of two valence electrons, it belongs to 2nd group.
Similarly, Q contains 3 shells and 7 valence electrons thus, it belongs to 3rd period and 17th (10 + 7) group.
The molecular formula of compound formed when P reacts with Q will be :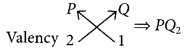
Question 40.
Write the number of periods and groups in the Modern Periodic Table. How does the metallic character of elements vary on moving (i) from left to right in a period, and
(ii) down a group? Give reason to justify your answer. (AI 2017)
Answer:
In the Modern periodic table, there are 18 vertical columns called groups and 7 horizontal rows called periods.
Trend of metallic character :
(i) Along the period from left to right: Metallic character of elements decreases as we move from left to right in a period. Metallic character depends on the electropositive character (tendency to loose electrons) of the elements. As we go across the period from left to right, one electron is added to same shell at every stage which increases the effective nuclear charge and hence, valence electrons becomes more and more closer to the nucleus. Due to this, the tendency of atoms to loose valence electrons and form positive ions decreases. Hence, electropositive character decreases resulting in decrease of metallic character.
(ii) Down the group : Metallic character of elements increases on moving down the group as the electropositive character increases down the group.
Question 41.
Na, Mg and Al are the elements of the 3rd periods of the Modern Periodic Table having group number 1,2 and 13 respectively. Which one of these elements has the
(a) highest valency, (b) largest atomic radius, and (c) maximum chemical reactivity? Justify your answer stating the reason for each. (AI 2017)
Answer:
Period number of Na, Mg and Al = 3
Group numbers of Na, Mg and Al are 1, 2 and 13 respectively.
(a) Aluminium (Al) will show highest valency of +3 as it belongs to group number 13 (valency = 13 – 10 = 3). Moreover, along the period from left to right valency first increases to maximum (+4) and then decreases.
(b) Sodium (Na) will have the largest atomic radius because as we move along the period from left to right, the atomic radius decreases.
(c) Sodium (Na) will have maximum chemical reactivity because as we move along the period from left to right, chemical reactivity of metals decreases.
Question 42.
Calcium is an element with atomic number 20. Stating reason answer each of the following questions:
(i) Is calcium a metal or non-metal?
(ii) Will its atomic radius be larger or smaller than that of potassium with atomic number 19?
(iii) Write the formula of its oxide. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Given that, atomic number of calcium is 20.
So, its electronic configuration = 2, 8, 8, 2 .
(i) As, it has 2 valence electrons in the outermost shell which can be easily lost, so it is a metal.
(ii) Atomic number of K (potassium) is 19 so, it is placed before Ca(20) in the same period.
On moving from left to right in a period, the atomic radius decreases.
Hence, atomic radius of Ca(20) will be smaller than that of K(19).
(iii) The valency of calcium as well as oxygen is 2 thus, the formula of the oxide will be CaO.
Question 43.
An element M with electronic configuration (2, 8, 2) combines separately with (NO
Answer:
Electronic configuration of M is 2, 8, 2 which shows that it belongs to group 2 and period 3 of the Modern periodic table.
As it has 2 valence electrons, so the valency of element M will be 2.
The chemical formulae of the compounds formed will be
M(NO3)2,MSO4, M3(PO4)2
As M has two valence electrons, it can easily loose these electrons to attain a noble gas configuration. Hence, M will form ionic compounds.
Question 44.
Name any two elements of group one and write their electronic configurations. What similarity do you observe in their electronic configurations? Write the formula of oxide of any of the aforesaid element. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Two elements of group 1 are sodium (Na) and potassium (K).
Electronic configuration of Na (11) = 2, 8, 1
Electronic configuration of K (19) = 2, 8, 8, 1
From the electronic configuration, we observe that both (Na and K) have one electron in outermost shell due to which they have valency equal to one.
Thus, formula of their oxides are, Na2O and K2O.
Question 45.
Two elements A and B belong to the 3rd period of Modern Periodic Table and are in group 2 and 13 respectively. Compare their following characteristics in tabular form.
(a) Number of electrons in their atoms
(b) Size of their atoms
(c) Their tendencies to loose electrons
(d) The formula of their oxides
(e) Their metallic characters
(f) The formula of their chlorides (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Electronic configuration of A = 2, 8, 2 i.e., Mg
Electronic configuration of B = 2, 8, 3 i.e., Al
| Characteristics | A | B |
| (a) No. of electrons in their atoms | 12 | 13 |
| (b) Size of their atoms | Bigger | Smaller |
| (c) Tendency to loose electrons | More | Less |
| (d) Formula of their oxides | AO | B2O3 |
| (e) Metallic character | More | Less |
| (f) Formula of their chlorides | ACl2 | BCl2 |
Question 46.
An element ‘X’ belongs to 3rd period and group 16 of the Modern Periodic Table.
(a) Determine the number of valence electrons and the valency of ‘X
(b) Molecular formula of the compound when ‘X’ reacts with hydrogen and write its electron dot structure.
(c) Name the element ‘X’ and state whether it is metallic or non-metallic. (AI 2016)
Answer:
(a) As the element ‘X’ belongs to 3rd period so, it will have three energy shells. Moreover, it belongs to 16th group, so it will have six valence electrons.
∴ Electronic configuration of X = 2, 8, 6
Thus, valence electrons = 6 and valency = 8 – 6 = 2
(b) Molecular formula of the compound formed when X reacts with hydrogen = H2X The electron dot structure is as :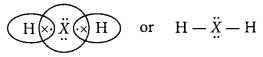
(c) The element X is sulphur and it is a non-metal.
Question 47.
An element ‘X’ has mass number 35 and number of neutrons 18. Write atomic number and electronic configuration of ‘X’ Also write group number, period number and valency of X. (AI 2016)
Answer:
Mass number of X = 35
Number of neutrons = 18
∴ Number of electrons = Number of protons – (Mass number – Number of neutrons)
= 35 – 18 = 17
Number of electrons of X = Atomic number of X= 17
Thus, electronic configuration of X = 2, 8, 7 As it has 7 electrons in the outermost shell, so it belongs to 17th group. Moreover the electrons are present in three shells, so it belongs to 3rd period. Valency of X = 8 – 7 = 1
Question 48.
Three elements ‘X\ ‘Y’ and ‘Z’ have atomic numbers 7, 8 and 9 respectively.
(a) State their positions (group number and period number both) in the Modern Periodic Table.
(b) Arrange these elements in the decreasing order of their atomic radii.
(c) Write the formula of the compound formed when X’ combines with ‘Z’. (AI 2016)
Answer:
(a) For element X of atomic number 7, the electronic configuration is 2, 5 so it has 5 valence electrons and hence, it belongs to group 15. As seven electrons are filled in two shells so, it belongs to 2nd period.
Similarly, for Y(8), electronic configuration = 2, 6
Period number = 2, Group number = 16 and for Z(9) = 2, 7
Period number = 2, Group number = 17
(b) As size of the atoms decreases on moving from left to right in a period so, the order of atomic radii will be : X > Y > Z
(c) Formula of the compound when X combines with Z: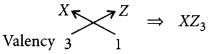
Question 49.
The position of eight elements in the Modern Periodic Table is given below where atomic numbers of elements are given in the parenthesis.
| Period No | ||
| 2 | Li (3) | Be (4) |
| 3 | Na (11) | Mg (12) |
| 4 | K (19) | Ca (20) |
| 5 | Rb (37) | Sr (38) |
Write the electronic configuration of Ca.
(ii) Predict the number of valence electrons in Rb.
(iii) What is the number of shells in Sr?
(iv) Predict whether K is a metal or a non-metal?
(v) Which one of these elements has the largest atom in size?
(vi) Arrange Be, Ca, Mg and Rb in the increasing order of the size of their respective atoms. (AI 2016)
Answer:
(i) Atomic number of Ca = 20
∴ Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 8, 2
(ii) Rb (37), electronic configuration = 2, 8, 18, 8, 1
Thus, number of valence electrons = 1
(iii) As Sr (38) belongs to period number 5 so, it will have 5 shells.
(iv) As K(19) = 2, 8, 8, 1
s0, it has 1 valence electron which can be easily lost to attain the noble gas configuration. Hence, potassium (K) is a metal.
(v) Size of the atom increases down the group and decreases from left to right along a period. Thus, Rb (37) will be the largest atom among given elements.
(vi) Increasing order of atomic size is Be < Mg < Ca < Rb
Question 50.
An element ‘X’ belongs to 3rd period and group 13 of the Modern Periodic Table.
(a) Determine the valence electrons and the valency of ‘X’.
(b) Molecular formula of the compound formed when ‘X’ reacts with an element ‘Y’ (atomic number = 8)
(c) Write the name and formula of the compound formed when ‘X’ combines with chlorine. (AI 2016)
Answer:
(a) As X belongs to group 13 so, it will have three valence electrons and valency of X will be 3.
(b) Atomic number of Y = 8
∴ Electronic configuration = 2, 6
Valency of Y = 8 – 6 = 2
Molecular formula of the compound when X reacts with element Y: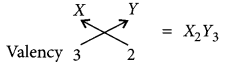
(c) As X belongs to 3rd period and group number 13, so it will be aluminium (Al).
For chlorine (17), electronic configuration = 2,8,7
∴ Valency of Cl = 8 – 7 = 1
∴ Formula of the compound :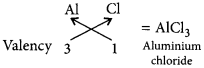
Question 51.
State the main aim of classifying elements. Which is the more fundamental property of elements that is used in the development of Modern Periodic Table? Name and state the law based on this fundamental property. On which side of the periodic table one can find metals, non-metals and metalloids? (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
The main aim of classifying elements is the prediction of their properties with more precision (systematic study of known elements).
When the elements are arranged on the basis of increasing atomic number then it is easier to predict their properties. This led to the development of Modern periodic table. Modern periodic law states that the properties of elements are periodic function of their atomic numbers.
In Modern periodic table, the metals like sodium and magnesium are towards left hand side while the non-metals like sulphur and chlorine are found on the right hand side. Elements like silicon, germanium, etc. which lie along the border line (group 13 to group 16) are semi-metals or metalloids because they exhibit some properties of both metals and non-metals.
Question 52.
An element ‘X’ (atomic number 20) burns in the presence of oxygen to form a basic oxide.
(a) Identify the element and write its electronic configuration.
(b) State its group number and period number in the Modern Periodic Table.
(c) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction when this oxide is dissolved in water. (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
(a) Atomic number of element X is 20 so, it is calcium (Ca).
Electronic configuration of Ca = 2, 8, 8, 2
(b) As calcium has two valence electrons in its outermost shell, so it belongs to group 2.
Moreover, it has four shells which indicates that it belongs to period number 4.
(c) Calcium forms a basic oxide having the formula: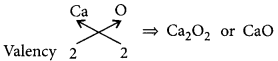
When calcium oxide is treated with water then calcium hydroxide is formed.![]()
Question 53.
An element ‘X’ belongs to third period and second group of the Modern Periodic Table.
(a) Write its electronic configuration.
(b) Is it a metal or non-metal? Why?
(c) Write the formula of the compound formed when ‘X’ reacts with an element
(i) Y of electronic configuration 2, 6 and
(ii) Z of electronic configuration 2, 8, 7. (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Third period indicates that it has three shells while group 2 indicates that it has two valence electrons in its outermost shell.
Thus, X must be magnesium (Mg).
(a) Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 2
(b) As X has two valence electrons in its outermost shell which can be easily lost to form a noble gas configuration, so it is a metal.
(c) (i) Electronic configuration of Y = 2, 6 Hence, valency of Y = 8 – 6 = 2
Formula of compound formed when X reacts with Y is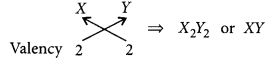
(ii) Electronic configuration of Z = 2, 8, 7
Hence, valency of Z = 8 – 7 = l
Formula of compound formed when X reacts with Z is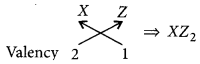
Question 54.
The atomic number of an element X is 19.
(a) Write its electronic configuration.
(b) To which period of the Modern Periodic Table does it belong and what is its valency?
(c) If ‘X’ burns in oxygen to form its oxide, what will be its nature – acidic, basic or neutral?
Write balanced chemical equation for the reaction when this oxide is dissolved in water. (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Atomic number of X = 19
(a) Electronic configuration of X = 2, 8, 8,1
(b) X has four shells so, the period number of X = 4. Moreover, it has one electron in its outermost shell, so the valency of X will be equal to one.
(c) Electronic configuration of X shows that it is a metal and metals form basic oxides.
(d) When oxide of X is dissolved in water then its hydroxide will be formed.
X2O + H2O → 2XOH
Question 55.
How does the tendency of the elements to loose electrons change in the Modern Periodic Table in (i) a group, (ii) a period and why? (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
(i) Tendency of the elements to loose electrons increases down the group. The reason being that at each succeeding element down a group, the number of shells increases. So, the distance of the valence shell from the nucleus increases due to which the effective nuclear charge decreases on the last shell of electrons. So, it becomes easier for the atom to loose electrons.
(ii) Tendency of the elements to loose electrons decreases in a period from left to right. The reason being that as the electron enters to the same shell at each successive element the effective nuclear charge on the valence shell electron increases, the attraction between the valence electrons and nucleus increases so, it becomes difficult to loose electrons.
Question 56.
How many groups and periods are there in the Modern Periodic Table? How do the atomic size and metallic character of elements vary as we move:
(a) down a group and
(b) from left to right in a period? (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
There are 18 groups and 7 periods in the Modern periodic table.
Atomic size increases down the group, while moving from left to right in a period it decreases.
Metallic character of elements increases down the group while moving from left to right in a period it decreases.
Question 57.
Na, Mg and A1 are the elements of the same period of Modern Periodic Table having one, two and three valence electrons respectively. Which of these elements (i) has the largest atomic radius, (ii) is least reactive? Justify your answer stating reason for each case. (Delhi 2015, AI 2012)
Answer:
Na, Mg and A1 belong to same period of Modern periodic table.![]()
(i) Sodium (Na) will have the largest atomic radius because as we move from left to right in a period, atomic size decreases due to increase in effective nuclear charge which pulls the outermost electrons more closer to the nucleus.
(ii) Aluminium (Al) is least reactive because on moving from left to right in the periodic table the nuclear charge increases, so the valence electrons are pulled more closer to the nucleus. Therefore, the tendency to loose electrons decreases and hence, reactivity decreases.
Question 58.
From the following elements :
4Be; 9F; 19K; 20Ca
(i) Select the element having one electron in the outermost shell.
(ii) Two elements of the same group.
Write the formula and mention the nature of the compound formed by the union of 19K and element X (2, 8, 7). (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 28.
The, formula of compound when K combines with X is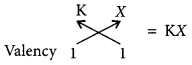
As K has one electron in its outermost shell, so it transfers this electron to outermost shell of X and hence, an ionic compound is formed.![]()
Question 59.
Write the number of periods the Modern Periodic Table has. State the changes in valency and metallic character of elements as we move from left to right in a period. Also state the changes, if any, in the valency and atomic size of elements as we move down a group. (Delhi 2015, 2013)
Answer:
There are 7 periods in the Modern periodic table.
As we move along the period from left lo right then valency of the elements first increases from 1 to 4 and then decreases to 0.
On moving from left to right in a period the metallic character of elements decreases as the electropositive character of elements decreases across the period.
On moving down the group, the valency of the elements remains the same while atomic size increases. This is due to addition of new shell of electrons at every successive step.
Question 60.
Two elements ‘P’ and ‘Q’ belong to the same period of the Modern Periodic Table and are in Group-1 and Group-2 respectively. Compare their following characteristics in tabular form:
(a) The number of electrons in their atoms.
(b) The sizes of their atoms.
(c) Their metallic character.
(d) Their tendencies to loose electrons.
(e) The formula of their oxides.
(f) The formula of their chlorides. (AI 2015)
Answer:
The given characteristics can be tabulated as follows: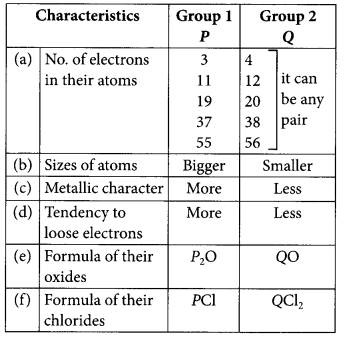
Question 61.
Taking the example of an element of atomic number 16, explain how the electronic configuration of the atom of an element relates to its position in the Modern Periodic Table and how valency of an element is calculated on the basis of its atomic number. (AI 2015)
Answer:
Atomic number of the element = 16
Thus, electronic configuration = 2, 8, 6
Since, this element contains 3 shells hence, it belongs to period number 3.
As the element has 6 valence electrons, group number = 10 + 6 = 16
The valency of an element is determined by the number of electrons present in the outermost shell.
∴ Valency of the element = 8 – valence electrons
= 8 – 6 = 2
Question 62.
Given below are some elements of the Modern Periodic Table. Atomic number of the element is given in the parentheses : A(4),B(9),C(14),D(19),£(20)
(a) Select the element that has one electron in the outermost shell. Also write the electronic configuration of this element.
(b) Which two elements amongst these belong to the same group? Give reason for your answer.
(c) Which two elements amongst these belong to the same period? Which one of the two has bigger atomic radius? (AI 2015)
Answer:
The electronic configuration of the given elements will be as follows :
A(4) = 2, 2
B(9) = 2, 7
C(14) = 2, 8,4
D(19) = 2, 8, 8,1
E(20) = 2, 8, 8, 2
(a) Element D will have one electron in its outermost shell.
(b) Elements A and E will belong to same group as both of them have same electrons in their outermost shells.
(c) A and B belong to period number 2 (two shells). A has bigger atomic radius than B.
D and E belong to period number 4 (four shells). D has bigger atomic radius than E.
Question 63.
The atomic number of an element ‘X’ is 20.
(i) Determine the position of the element X in the periodic table.
(ii) Write the formula of the compound formed when ‘X’) reacts/combines with another elements ‘Y’ (atomic number 8).
(iii) What would be the nature (acidic or basic) of the compound formed? Justify your answer. (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 52.
Question 64.
An element X is placed in the 3rd group and 3rd period of the Modern Periodic Table. Answer the following questions stating reason for your answer in each case :
(a) Write the electronic configuration of the element X.
(b) Write the formula of the compound formed when the element X reacts with another element ‘Y’ of atomic number 17.
(c) Will the oxide of this element be acidic or basic? (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
X is placed in 3rd group (IIIA) and 3rd period of the Modern periodic table then it must be aluminium (Al).
As it belongs to 3rd group so it will have 3 electrons in its outermost shell.
Also it belongs to 3rd period, so it will have 3 shells.
(a) Electronic configuration of X = 2, 8, 3
(b) Atomic number of Y = 17
Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 7
Valency of V = 8 – 7 = 1
Formula of compound formed when X reacts with Y: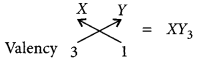
(c) Al2O3 is amphoteric in nature i.e., acidic as well as basic oxide.
Question 65.
Four elements P, Q, R and S belong to the third period of the Modern Periodic Table and have respectively 1, 3, 5 and 7 electrons in their outermost shells. Write the electronic configurations of Q and R and determine their valencies. Write the molecular formula of the compound formed when P and S combine. (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
P, Q, R and S all belong to 3rd period so, all of them will have 3 shells and the number of electrons in their outermost shell is 1, 3,5 and 7 respectively.
∴ Electronic configuration of Q = 2, 8, 3 and its valency = 3
Similarly, electronic configuration of R = 2, 8, 5
and its valency = 8 – 5 = 3
Electronic configuration of P = 2, 8, 1
Thus, valepcy of P = 1
Electronic configuration of S = 2, 8, 7
Thus, valency of S = 8 – 7 = 1
Molecular formula of the compound :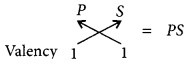
Question 66.
In the following table, the positions of six elements A, B, C, D, E and F are given as they are in the Modern Periodic Table :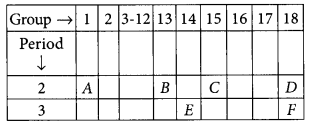
On the basis of the above table, answer the following questions:
(i) Name the element which forms only covalent compounds.
(ii) Name the element which is a metal with valency three.
(iii) Name the element which is a non-metal with valency three.
(iv) Out of B and C, whose atomic radius is bigger and why?
(v) Write the cbmmon name for the family to which the elements D and F belong. (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
(i) Element E will form only covalent compounds because it has 4 electrons in the outermost shell so, it can neither loose nor gain 4 electrons, hence E forms compounds by sharing of electrons.
(ii) Element E is a metal having valency 3 as it belongs to group 13.
(iii) C is a non-metal with valency (8 – 5 = 3).
(iv) Out of B and C, B will be bigger in size because as we move along the period from left to right, the atomic radius decreases due to addition of electrons in the same shell at each successive element. Hence, nucleus pulls electrons more towards the centre.
(v) D and E belong to group 18 and are called noble gases.
Question 67.
Based on the group valency of elements state the formula for the following giving justification for each:
(i) Oxides of 1st group elements,
(ii) Halides of the elements of group-13, and
(iii) Compounds formed when an element of group-2 combines with an element of group-16. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Refer to answer 37(i).
(ii) Refer to answer 37(ii).
(iii) Compounds formed when element of group-2 combines with an element of group-16 :
Let the group-2 element be X and group-16 element be Y.
Valency of X = 2
Valency of Y = 2
Chemical formula of the compound will be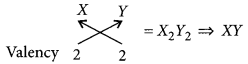
Question 68.
(a) Define the following terms :
(i) Valency; (ii) Atomic size
(b) How do the valency and the atomic size of the elements vary while going from left to right along a period in the Modern Periodic Table? (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(a) (i) Valency: It is defined as the combining capacity of the element which is determined by the number of valence electrons present in the outermost shell of its atom.
(ii) Atomic size : It is defined as the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell of an isolated atom.
(b) On moving from left to right in the period, the valency of elements increases from 1 to 4 and then decreases to 0.
This is because the elements in a period do not have the same number of valence electrons hence, they do not show same valency.
The atomic size decreases on moving from left to right along a period due to increase in nuclear charge which tends to pull the electrons closer to the nucleus and reduces the size of the atom.
Question 69.
Consider two elements X (atomic number 17) and Y (atomic number 20).
(i) Write the positions of these elements in the Modern Periodic Table giving justification.
(ii) Write the formula of the compound formed by the combination of X and Y.
(iii) Draw the electron-dot structure of the compound formed and state the nature of the bond formed between the two elements. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Atomic number of X = 17
Electronic configuration of X = 2, 8, 7
Atomic number of Y = 20
Electronic configuration of Y = 2, 8, 8, 2
(i) From the electronic configurations, we can easily observe that X contains 3 shells so, it belongs to period 3 and it contains 7 electrons in the outermost shell so, it belongs to group-17. Similarly for Y, it has 4 shells which implies that it belongs to period 4 and Y contains two electrons in the outermost shell so, it belongs to group-2.
(ii) Valency of X = 1
Valency of Y = 2
Thus, formula of the compound formed will be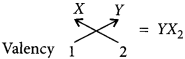
(iii) Electron dot structure of the compound will be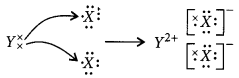
As two electrons present in the outermost shell of Y are donated to two different atoms of X thus, it will be an ionic bond (formed by the complete transfer of electrons).
Question 70.
Consider two elements ‘A’ (Atomic number 17) and ‘B’ (Atomic number 19).
(i) Write the positions of these elements in the Modern Periodic Table giving justification.
(ii) Write the formula of the compound formed when ‘A’ combines with ‘B’.
(iii) Draw the electron dot structure of the compound and state the nature of the bond formed between the two elements. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Atomic number of A = 17
Electronic configuration of A = 2, 8, 7
Atomic number of B = 19
Electronic configuration of B = 2, 8, 8, 1
(i) From the electronic configuration of A, it can be easily observed that A contains three shells which indicates that it belongs to period 3. Moreover, it has seven valence electrons in its outermost shell which indicates that it belongs to group 17.
Similarly for B, it has 4 shells so, it belongs to period 4 and it has one electron in outermost shell so, it belongs to group 1.
(ii) The molecular formula of the compound when A combines with B will be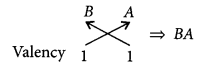
As A contains 7 electrons in the outermost shell so, it is an electropegative element that is why A is placed after B.
(iii) The electron dot structure will be![]()
The one electron present in the outermost shell of B gets transferred to the outermost shell of A and hence, ionic bond is formed.
Question 71.
The electrons in the atoms of four elements A, B, C and D are distributed in the three shells having 1, 3, 5 and 7 electrons in the outermost shell respectively. State the period in which these elements can be placed in the Modern Periodic Table. Write the electronic configuration of the atoms of A and D and the molecular formula of the compound formed when A and D combine. (AI 2014)
Answer:
Refer to answer 65.
Question 72.
Study the following table in which positions of six elements A, B, C, D, E and F are shown as they are in the Modern Periodic Table :
On the basis of the above table, answer the following questions: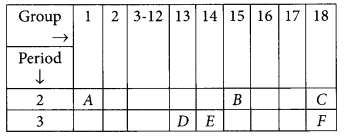
(i) Name the element which forms only covalent compounds.
(ii) Name the element which is a metal with valency three.
(iii) Name the element which is a non-metal with valency three.
(iv) Out of D and E, which is bigger in size and why?
(v) Write the common name for the family to which the elements C and F belong. (AI 2014)
Answer:
(i) Element E will form only covalent compounds because it has 4 electrons in the outermost shell so, it can neither loose nor gain 4 electrons, hence E forms compounds by sharing of electrons.
(ii) Element D is a metal having valency 3 as it belongs to group 13.
(iii) B is a non-metal with valency (8 – 5 = 3).
(iv) Out of D and E, D will be bigger in size because as we move from left to right in a period there is addition of extra electron in the same shell due to which electrons are pulled more closer to the nucleus.
(v) C and F belong to group 18 and are called noble gases.
Question 73.
What is meant by ‘group’ in the Modern Periodic Table? How do the following change on moving from top to bottom in a group?
(i) Number of valence electrons.
(ii) Number of occupied shells.
(iii) Size of atoms.
(iv) Metallic character of elements.
(v) Effective nuclear charge experienced by valence electrons. (AI 2014)
Answer:
The vertical columns in the Modern periodic table are called groups. There are total 18 groups in the Modern periodic table.
(i) In a particular group, the number of valence electrons remains the same.
(ii) On moving down the group, there is addition of an extra shell successively. Flence, number of occupied shells increases.
(iii) Due to addition of extra shells down the group, the size of the atoms i.e.. the distance between nucleus and the outermost shell also increases.
(iv) Down the group as atomic size increases, the outermost electron is pulled by nucleus to lesser extent and lienee, tendency to loose electrons increases i.e., metallic character increases.
(v) Effective nuclear charge experienced by valence electrons decreases down the group due to increase in size of atoms.
Question 74.
The elements Be, Mg and Ca each having two electrons in their outermost shells are in periods 2, 3 and 4 respectively of the Modern Periodic Table. Answer the following questions, giving justification in each case:
(i) Write the group to which these elements belong.
(ii) Name the least reactive element.
(iii) Name the element having largest atomic radius. (AI 2014)
Answer:
(i) As Be, Mg and Ca have two electrons in their outermost shell so, they all belong to group 2.
(ii) Be will be least reactive element, as down the group the reactivity of the metals increases. Be being smaller in size as compared to others will have less tendency to loose electrons and hence, is less reactive.
(iii) As we move down the group, atomic radius increases hence, calcium will have the largest atomic radius.
Question 75.
What are groups and periods in the periodic table? Two elements X and Y belong to group 1 and 2 respectively and are in the same period of the periodic table. How do the following properties of X and Y vary?
(i) Size of their atoms.
(ii) Their metallic character.
(iii) Their valencies in forming oxides.
(iv) Molecular formula of their chlorides. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
The horizontal rows of elements in the periodic table are called periods. There are seven periods in the long form of periodic table.
The vertical columns in a periodic table are called groups. There are 18 groups in the long form of periodic table.
X belongs to group-1 while Y belongs to group-2 of the same period hence, valency of X will be 1 and valency of Y will be 2.
(i) As we move along the period from left to right the size of the atoms decreases. Hence, X will be bigger than Y.
(ii) Across the period from left to right, the metallic character decreases. Hence, X is more metallic than Y.
(iii) The valency of X in its oxide will be 1 and that of Y in its oxide will be 2.
(iv) Molecular formula of their chlorides will be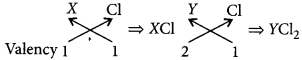
Question 76.
Write the number of groups and periods in the Modern Periodic Table. Mention the criteria of placing elements in the (i) same group and (ii) same period. Illustrate your answer with an example for each case. (Foreign 2014, Delhi 2013C)
Answer:
There are 18 groups and 7 periods in the Modern periodic table.
(i) For elements to be in the same group, they should have same number of electrons in their outermost shells. For example, sodium and potassium have one electron in their outermost shells, so they belong to same group i.e., group 1.
(ii) For elements to be in the same period, they should have same number of shells. For example, magnesium (12) and aluminium (13) contain three shells so, they belong to period 3.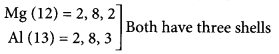
Question 77.
Study the following table in which positions of six elements A, B, C, D, E and F are shown as they are in the Modern Periodic Table :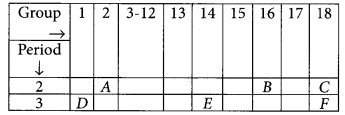
On the basis of the above table, answer the following questions:
(i) Name the element which will form only covalent compounds.
(ii) Which element is a metal with valency one?
(iii) Which element is a non-metal with valency two?
(iv) Out of D and E, which has a bigger atomic radius and why?
(v) Write the formula of the compound formed when B combines with D.
Answer:
(i) Element E will form only covalent compounds.
(ii) Element D is a metal with valency one as it belongs to group 1.
(iii) Element B is a non-metal with valency 2 as it belongs to group 16 (valency = 8-6 = 2).
(iv) Out of D and E, D will have bigger atomic radius because as we move along the period from left to right there is decrease in atomic radius.
(v) Valency of B = 2 Valency of D = 1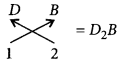
Question 78.
The electronic configuration of an element is 2, 8, 8, 1.
(i) State its group number and period number in the Modern Periodic Table.
(ii) State whether this element is a metal or a non-metal.
Give reason for the justification of your answer in each case. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
Electronic configuration of element = 2, 8, 8, 1
(i) It contains one electron in its outermost shell thus, it belongs to group 1. Moreover, the element has 4 shells, so it belongs to period 4.
(ii) As the element contains one electron in its outermost shell which can be easily lost hence, it acts as a metal.
Question 79.
Given below are some elements of the Modern Periodic Table:
4Be, 9F, 14Si, 19K, 20Ca
(i) Select the element that has one electron in the outermost shell and write its electronic configuration.
(ii) Select two elements that belong to the same group. Give reasons for your answer.
(iii) Select two elements that belong to the same period. Which one of the two has bigger atomic size? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(i), (ii) Refer to answer 28.
(iii) Be and F belong to the same period (period 2). K and Ca belong to the same period (period 4). Among Be and F, Be will be bigger in size and among K and Ca, K will be bigger in size.
Question 80.
An element ‘X’ belongs to the third period and group one of the Modern Periodic Table. Find (i) the number of its valence electrons (ii) its valency, and (iii) whether X is a metal or a non-metal. State reasons to justify your answer in each case. (Delhi 2013C)
Answer:
As element X belongs to group 1, thus it will have one electron in its outermost shell. Moreover, it belongs to period 3 which implies that X has 3 shells.
(i) Electronic configuration of X will be 2, 8,1 Hence, number of valence electrons = 1
(ii) Valency of X will be 1.
(iii) As X contains 1 valence electron which can be easily lost hence, it is a metal.
Question 81.
F, Cl and Br are the elements each having seven valence electrons. Which of these (i) has the largest atomic radius, (ii) is most reactive? Justify your answer stating reason for each. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(i) F, Cl and Br all have seven valence electrons so, they belong to the same group. On moving down the group, the atomic size of the elements increases due to addition of extra shell at each successive element. Due to this the average distance between nucleus and outermost electrons increases. Thus, Br is largest in size among F, Cl and Br.
(ii) Fluorine is the most reactive element because the chemical reactivity of non-metals decreases on going down a group as the size of the atoms goes on increasing. Hence, the attraction of incoming electrons decreases. Therefore, the tendency of atoms to gain electrons decreases due to which their reactivity decreases.
Question 82.
(a) How many periods are there in the Modern Periodic Table of elements?
(b) How do atomic radius, valency and metallic character vary down a group?
(c) How do the atomic size and metallic character of elements vary as we move from left to right in a period? (Foreign 2012)
Answer:
Refer to answer 56.
Valency remains the same in a group, as the number of valence electrons are same. Valency first increases from 1 to 4 in a period and then decreases to 0.
Question 83.
The atomic number of an element is 16. Predict
(i) the number of valence electrons in its atom
(ii) its valency
(iii) its group number
(iv) whether it is a metal or a non-metal
(v) the nature of oxide formed by it
(vi) the formula of its chloride. (AI 2011)
Answer:
Atomic number of element (E) = 16
∴ Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 6
(i) Number of valence electrons in the atom = 6
(ii) Valency =8-6 = 2
(iii) As there are 6 valence electrons thus, its group number is 10 + 6 = 16
(iv) This element is a non-metal.
(v) The nature of oxide formed by this element is acidic.
(vi) The formula of the chloride of non-metal ‘E‘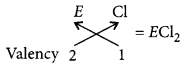
Question 84.
The positions of three elements A, B and C in the periodic table are indicated below :
| Group 16 | Group 17 | |
| – | – | (First period) |
| – | A | (Second period) |
| – | – | (Third period) |
| B | C | (Fourth period) |
(a) State whether element C would be a metal or a non-metal? Why?
(b) Which is the more active element A or C? Why?
(c) Which type of ion (cation or anion) will be formed by the element C? Why?
Answer:
(a) C belongs to group 17 and hence, it will have 7 valence electrons in the outermost shell and has a tendency to gain electrons thus, it is a non-metal.
(b) Among A and C, A will be more reactive as the reactivity decreases down the group in case of non-metals. So, A has more tendency to gain electrons.
(c) C will form negatively charged ion which is known as anion because group 17 elements have seven electrons in their outermost shell so, they have strong tendency to gain an electron to attain the noble gas configuration.
Question 85.
The position of certain elements in the modern periodic table are shown below :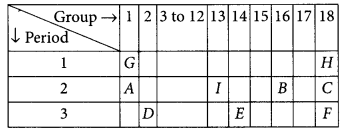
Using the above table answer the following
questions giving reasons in each case :
(i) Which element will form only covalent compounds?
(ii) Which element is a non-metal with valency 2?
(iii) Which element is a metal with valency 2?
(iv) Out of H, C and F which has largest atomic size? (2020)
(v) To which family does H, C and F belong?
Answer:
(i) Element E will form only covalent compounds because it has 4 electrons in the outermost shell so, it can neither loose nor gain 4 electrons, hence E forms compounds by sharing of electrons.
(ii) Element B is a non-metal with valency 2 as it belongs to group 16 (valency = 8 – 6 = 2).
(iii) Element D is a metal with valency two as it belongs to group 2.
(iv) Atomic size increases down the group hence F is largest in size.
(v) H, C and F belongs to noble gas as these are in group-18.
Question 86.
Define atomic size. Give its unit of measurement. In the modern periodic table what trend is observed in the atomic radius in a group and a period and why is it so? (2020)
Answer:
Atomic size : The distance from the center of the nucleus of an isolated atom from outermost shell containing electrons is known as atomic size. The unit of measurement is Angstrom (Å).
Refer to answer 56.
Question 87.
(a) How does metallic character of elements in Modern Periodic Table vary on moving from
(i) left to right in a period
(ii) top to bottom in a group?
Explain with the help of an example in each case.
(b) If an element X is placed in group-14, what will be the nature of bond in its chloride? Write the chemical formula of the compound formed.
(c) An element X has mass number = 35 and number of neutrons = 18. What is the atomic number of X? Write electronic configuration of X and determine its valency. (AI 2019)
Answer:
(a) Refer to answer 40.
Examples:
Variation of metallic character across the period :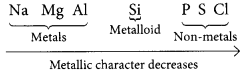
Variation of metallic character down the group :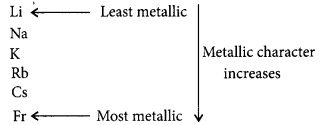
(b) Since element ‘X’ is placed in group 14, therefore, its valency is 14 – 10 = 4. Further, since it is difficult to either lose all the four valence electrons or gain four more electrons, therefore, it prefers to share these four electrons to acquire the stable electronic configuration of the nearest inert gas. Thus, the nature of the chloride of element ‘X is covalent and the chemical formula is XCl4.
(c) Refer to answer 47.
Question 88.
(a) The modern periodic table has been evolved through the early attempts of Dobereiner, Newlands and Mendeleev. List one advantage and one limitation of all the three attempts.
(b) Name the scientist who first of all showed that atomic number of an element is a more fundamental property than its atomic mass.
(c) State modern periodic law.
Answer:
(a) Advantage of Dobereiner’s triads : It recognised a relationship between properties of elements and their atomic weights.
Limitation of Dobereiner’s triads : Dobereiner could identify only three triads. He was not able to prepare triads of all the known elements.
Advantage of Newland’s law of octaves : This law provided a basis for the classification of elements into groups of elements having similar properties.
Limitation of Newlands’ law of octaves : This law worked only for the lighter elements. All the element discovered at that time could not be classified into octaves.
Advantage of Mendeleev’s periodic table : He classified all the 63 elements discovered at that time on the basis of similarities in their properties.
Limitation of Mendeleev’s periodic table : Increasing order of atomic masses could not be maintained in all cases e.g., cobalt with higher atomic mass was placed before nickel.
(b) Henry Moseley, an English physicist, showed that atomic number of an element is a more fundamental property than its atomic mass.
(c) Modern periodic law states that the physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic numbers.










