NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.1
Ex 13.1 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
2 cubes each of volume 64 cm3 are joined end to end. Find the surface area of the resulting cuboid.
Solution: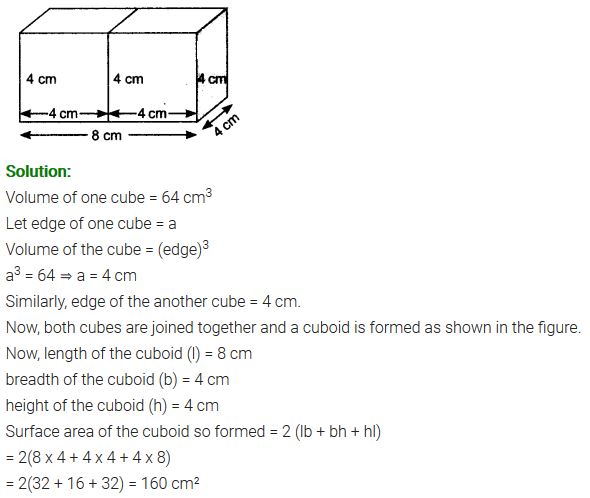
Ex 13.1 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
A vessel is in the form of a hollow hemisphere mounted by a hollow cylinder. The diameter of the hemisphere is 14 cm and the total height of the vessel is 13 cm. Find the inner surface area of the vessel.
Solution: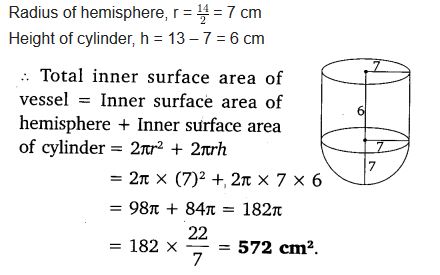
Ex 13.1 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
A toy is in the form of a cone of radius 3.5 cm mounted on a hemisphere of the same radius. The total height of the toy is 15.5 cm. Find the total surface area of the toy.
Solution: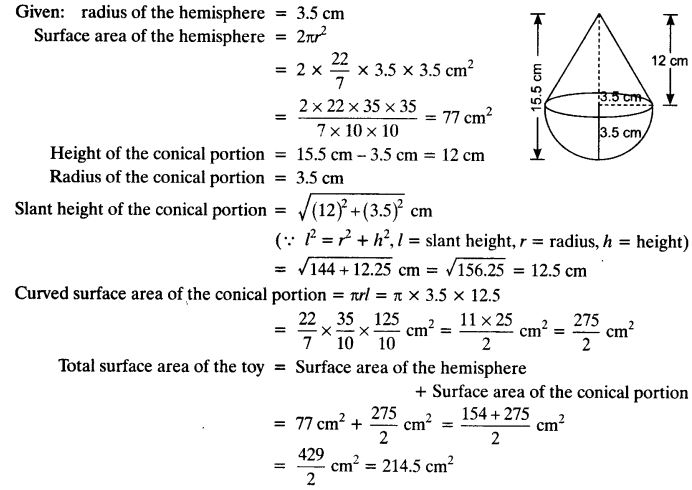
Ex 13.1 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
A cubical block of side 7 cm is surmounted by a hemisphere. What is the greatest diameter the hemisphere can have? Find the surface area of the solid.
Solution: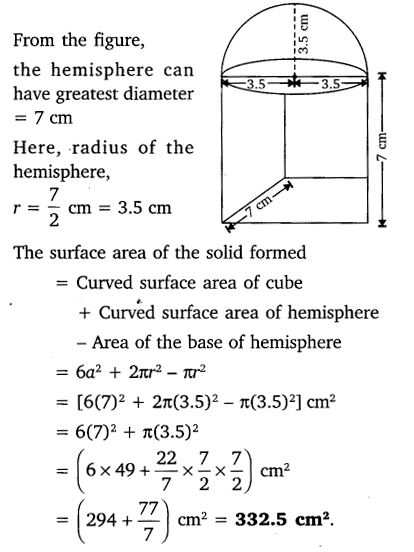
Ex 13.1 Class 10 Maths Question 5.
A hemispherical depression is cut out from one face of a cubical wooden block such that the diameter d of the hemisphere is equal to the edge of the cube. Determine the surface area of the remaining solid.
Solution: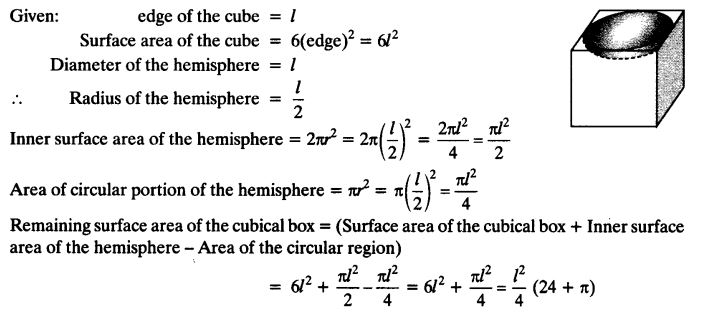
Ex 13.1 Class 10 Maths Question 6.
A medicine capsule is in the shape of a cylinder with two hemispheres stuck to each of its ends. The length of the entire capsule is 14 mm and the diameter of the capsule is 5 mm. Find its surface area.
Solution: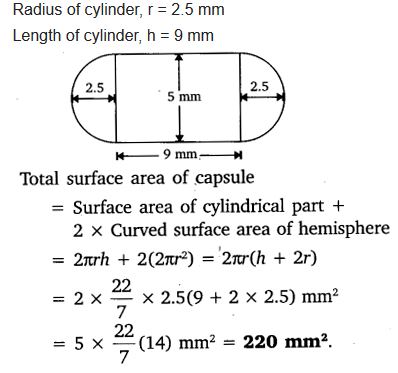
Ex 13.1 Class 10 Maths Question 7.
A tent is in the shape of a cylinder surmounted by a conical top. If the height and diameter of the cylindrical part are 2.1 m and 4 m respectively, and the slant height of the top is 2.8 m, find the area of the canvas used for making the tent. Also, find the cost of the canvas of the tent at the rate of Rs 500 per m2. (Note that the base of the tent will not be covered with canvas.)
Solution:
Ex 13.1 Class 10 Maths Question 8.
From a solid cylinder whose height is 2.4 cm and diameter 1.4 cm, a conical cavity of the same height and same diameter is hollowed out. Find the total surface area of the remaining solid to the nearest cm2.
Solution: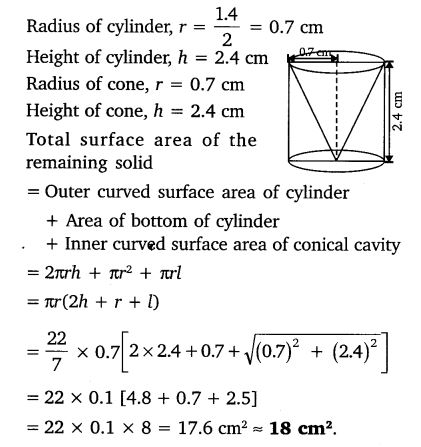
Ex 13.1 Class 10 Maths Question 9.
A wooden article was made by scooping out a hemisphere from each end of a solid cylinder, as shown in figure. If the height of the cylinder is 10 cm, and its base is of radius 3.5 cm, find the total surface area of the article.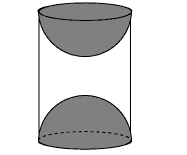
Solution: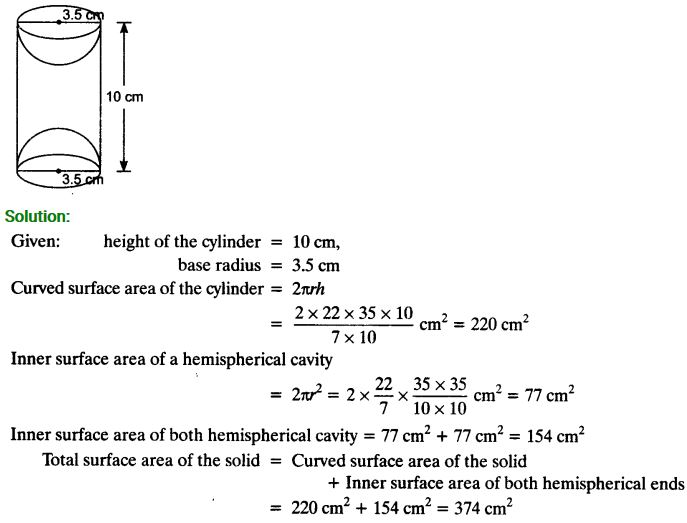
Class 10 Maths Surface Areas and Volumes Mind Maps
Surface Areas and Volumes of Solids
(i) Cuboid:
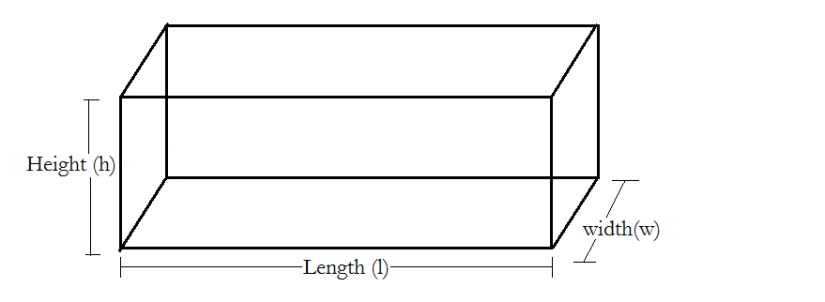
Volume = l × b × h
Total surface area = 2 [lb + bh + hl]
Lateral surface area = 2 [bh + hl]
Diagonal of the coboid =
(ii) Cube:
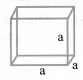
Volume = a3
Total surface area = 6a2
Lateral surface area = 4a2
Diagonal of a cube = √3a
(iii) Cylinder:
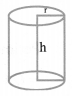
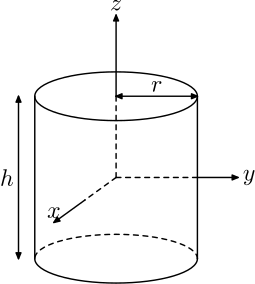
(a) Right circular cylinder:
Volume = πr2h
Curved Surface Area = 2nrh
Total Surface Area= 2πrh + 2πr2 = 2πr(r + h)
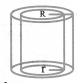
(b) Right circular hollow cylinder:
Let r and R be internal & external radii.
Volume = n(R2 – r2)h
Curved Surface Area = 2π(R + r)h
Total Surface Area = 2π(R + r)h + 2π(R2 – r2)
= 2π(R + r)(h + R — r)
(iv) Right circular cone:
Slant height, l = 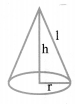
Volume =
Curved Surface Area = πrl
Total Surface Area = πrl + πr2
Surface Areas and Volumes of Sphere and Hemisphere
(i) Sphere:
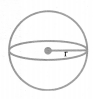
Volume =
Surface area =4πr2
(ii) Hemisphere:

Volume =
C.S.A = 2πr2
T.S.A = 3πr2
(iii) Hemispherical shell:
Volume =
Curved Surface Area = 2π(R2 + r2)
Total Surface Area = 2π(r2 + R2) + n (R2 – r2)
= π (r2 + 3R2)
Surface Areas of a Combination of Solids
The surface area of a solid which is a combination of two or more solids is calculated by adding the surface areas of the individual solids which are visible in the new solid formed.
For Example: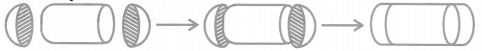
If we consider the surface of the newly formed object as given in the figure above, we would be able to see only the curved surfaces of the two hemispheres and the curved surface of the cylinder.
So, the total surface area of the new solid is the sum of the curved surface areas of each of the individual parts. This gives, TSA of new solid = CSA of one hemisphere + CSA of cylinder + CSA of other hemisphere
Volume of a Combination of Solids
Whenever solid is formed by combining two or more solids, then the amount of matter present in the new solid is equal to the sum of amounts of matter in the constituting solids. Volume of new solid = sum of the volumes of the individual solids
Conversion of Solid form One Shape to Another
(i) When a solid is converted from one shape to other, then its volume remains same only its shape and size changes.
(ii) If a solid is converted into a number of small identical solids, then Number of small items
Frustum of a Cone [Very Important for Board Exam]
When we slice (or cut) through a cone with a plane parallel to its base (see below figure ) and remove the cone that is formed on one side of that plane, the part that is now left over on the other side of the plane is called a frustum of the cone.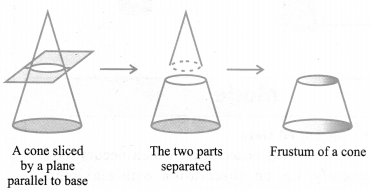
(i) Volume of the frustum of cone
(ii) C.S.A. of the frustum of cone = π(r1 + r2)l,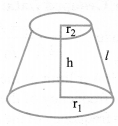
where l =
(iii) T.S.A. of the frustum of cone
l =
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.2
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.2 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.2
Ex 13.2 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
A solid is in the shape of a cone standing on a hemisphere with both their radii being equal to 1 cm and the height of the cone is equal to its radius. Find the volume of the solid in terms of π.
Solution: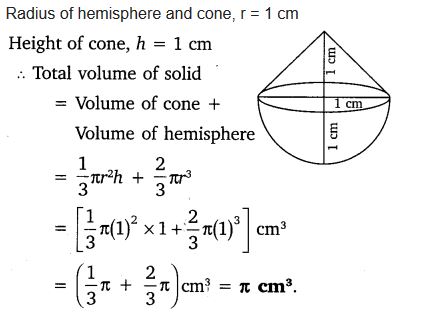
Ex 13.2 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
Rachel, an engineering student, was asked to make a model shaped like a cylinder with two cones attached at its two ends by using a thin aluminium sheet. The diameter of the model is 3 cm and its length is 12 cm. If each cone has a height of 2 cm, find the volume of air contained in the model that Rachel made. (Assume the outer and inner dimensions of the model to be nearly the same.)
Solution: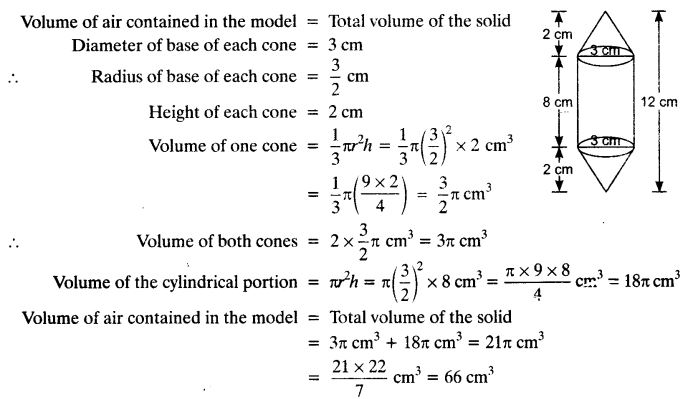
Ex 13.2 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
A gulab jamun, contains sugar syrup up to about 30% of its volume. Find approximately how much syrup would be found in 45 gulab jamuns, each shaped like a cylinder with two hemispherical ends with length 5 cm and diameter 2.8 cm.
Solution:
Ex 13.2 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
A pen stand made of wood is in the shape of a cuboid with four conical depressions to hold pens. The dimensions of the cuboid are 15 cm by 10 cm by 3.5 cm. The radius of each of the depressions is 0.5 cm and the depth is 1.4 cm. Find the volume of wood in the entire stand.
Solution: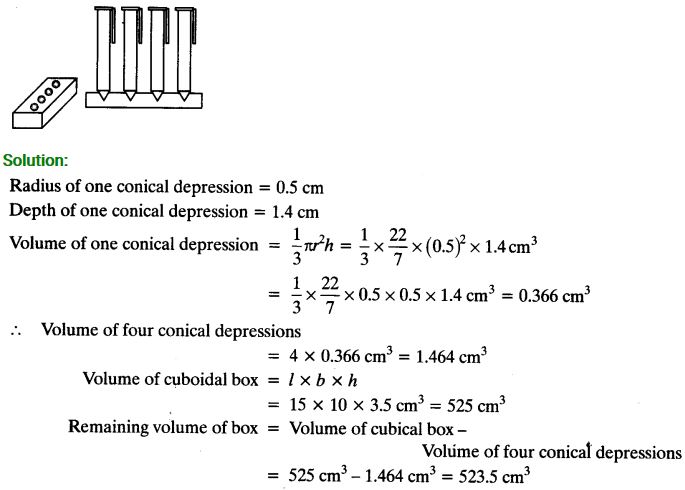
Question 5.
A vessel is in the form of an inverted cone. Its height is 8 cm and the radius of its top, which is open, is 5 cm. It is filled with water up to the brim. When lead shots, each of which is a sphere of radius 0.5 cm are dropped into the vessel, one-fourth of the water flows out. Find the number of lead shots dropped in the vessel.
Solution:
Ex 13.2 Class 10 Maths Question 6.
A solid iron pole consists of a cylinder of height 220 cm and base diameter 24 cm, which is surmounted by another cylinder of height 60 cm and radius 8 cm. Find the mass of the pole, given that 1 cm3 of iron has approximately 8g mass.
Solution: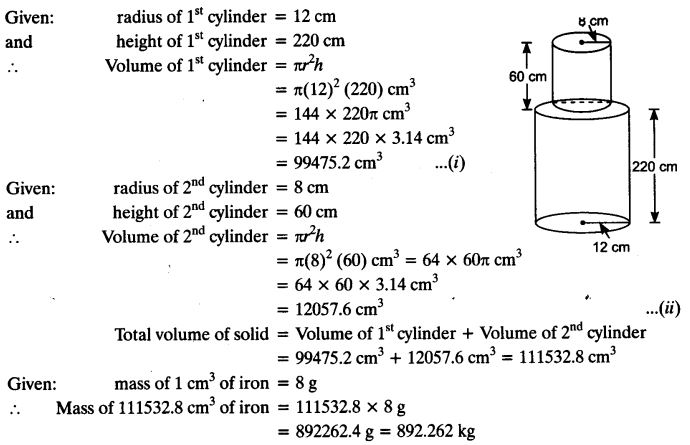
Ex 13.2 Class 10 Maths Question 7.
A solid consisting of a right circular cone of height 120 cm and radius 60 cm standing on a hemisphere of radius 60 cm is placed upright in a right circular cylinder full of water such that it touches the bottom. Find the volume of water left in the cylinder, if the radius of the cylinder is 60 cm and its height is 180 cm.
Solution:
Ex 13.2 Class 10 Maths Question 8.
A spherical glass vessel has a cylindrical neck 8 cm long, 2 cm in diameter; the diameter of the spherical part is 8.5 cm. By measuring the amount of water it holds, a child finds its volume to be 345 cm3. Check whether she is correct, taking the above as the inside measurements, and π = 3.14.
Solution: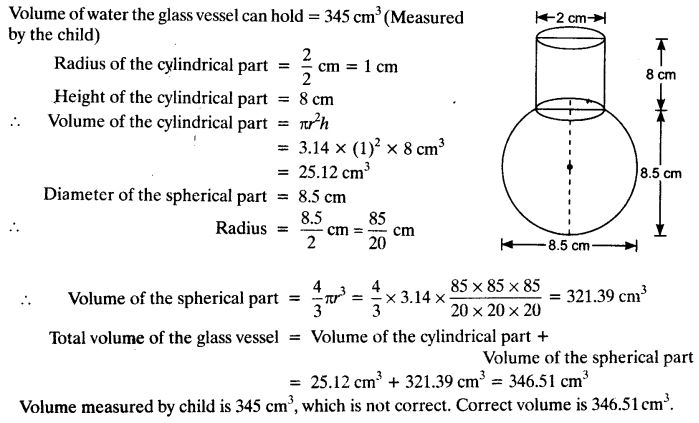
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.3
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.3 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.3
Ex 13.3 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
A metallic sphere of radius 4.2 cm is melted and recast into the shape of a cylinder of radius 6 cm. Find the height of the cylinder.
Solution:
Ex 13.3 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
Metallic spheres of radii 6 cm, 8 cm and 10 cm, respectively, are melted to form a single solid sphere. Find the radius of the resulting sphere.
Solution:
Download NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes PDF
Ex 13.3 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
A 20 m deep well with diameter 7 m is dug and the earth from digging is evenly spread out to form a platform 22 m by 14 m. Find the height of the platform.
Solution:
Ex 13.3 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
A well of diameter 3 m is dug 14 m deep. The earth taken out of it has been spread evenly all around it in the shape of a circular ring of width 4 m to form an embankment. Find the height of the embankment.
Solution:
Ex 13.3 Class 10 Maths Question 5.
A container shaped like a right circular cylinder having diameter 12 cm and height 15 cm is full of ice cream. The ice cream is to be filled into cones of height 12 cm and diameter 6 cm, having a hemispherical shape on the top. Find the number of such cones which can be filled with ice cream.
Solution:
Ex 13.3 Class 10 Maths Question 6.
How many silver coins, 1.75 cm in diameter and of thickness 2 mm, must be melted to form a cuboid of dimensions 5.5 cm × 10 cm × 3.5 cm?
Solution:
Ex 13.3 Class 10 Maths Question 7.
A cylindrical bucket, 32 cm high and with radius of base 18 cm, is filled with sand. This bucket is emptied on the ground and a conical heap of sand is formed. If the height of the conical heap is 24 cm, find the radius and slant height of the heap.
Solution: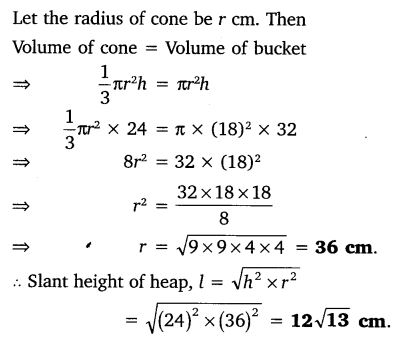
Ex 13.3 Class 10 Maths Question 8.
Water in a canal, 6 m wide and 1.5 m deep, is flowing with a speed of 10 km/h. How much area will it irrigate in 30 minutes, if 8 cm of standing water is needed?
Solution:
Ex 13.3 Class 10 Maths Question 9.
A farmer connects a pipe of internal diameter 20 cm from a canal into a cylindrical tank in her field, which is 10 m in diameter and 2 m deep. If water flows through the pipe at the rate of 3 km/h, in how much time will the tank be filled?
Solution:
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.4
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.4 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.4
Ex 13.4 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
A drinking glass is in the shape of a frustum of a cone of height 14 cm. The diameters of its two circular ends are 4 cm and 2 cm. Find the capacity of the glass.
Solution:
Ex 13.4 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
The slant height of a frustum of a cone is 4 cm and the perimeters (circumference) of its circular ends are 18 cm and 6 cm. Find the curved surface area of the frustum.
Solution:
Download NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes PDF
Ex 13.4 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
A fez, the cap used by the Turks, is shaped like the frustum of a cone. If its radius on the open side is 10 cm, radius at the upper base is 4 cm and its slant height is 15 cm, find the area of material used for making it.
Solution:
Ex 13.4 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
A container, opened from the top and made up of a metal sheet, is in the form of a frustum of a cone of height 16 cm with radii of its lower and upper ends as 8 cm and 20 cm, respectively. Find the cost of the milk which can completely fill the container, at the rate of Rs 20 per litre. Also find the cost of metal sheet used to make the container, if it costs Rs 8 per 100 cm2.
Solution:
Ex 13.4 Class 10 Maths Question 5.
A metallic right circular cone 20 cm high and whose vertical angle is 60 is cut into two parts at the middle of its height by a plane parallel to its base. If the frustum so obtained be drawn into a wire of diameter 1/16 cm, find the length of the wire.
Solution: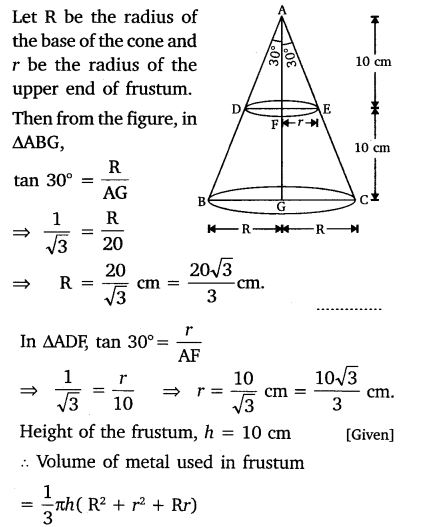

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.5
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.5 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.5
Ex 13.5 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
A copper wire, 3 mm in diameter is wound about a cylinder whose length is 12 cm, and diameter 10 cm, so as to cover the curved surface of the cylinder. Find the length and mass of the wire, assuming the density of copper to be 8.88 g per cm3.
Solution:
Ex 13.5 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
A right triangle, whose sides are 3 cm and 4 cm (other than hypotenuse) is made to revolve about its hypotenuse. Find the volume and surface area of the double cone so formed.
Solution: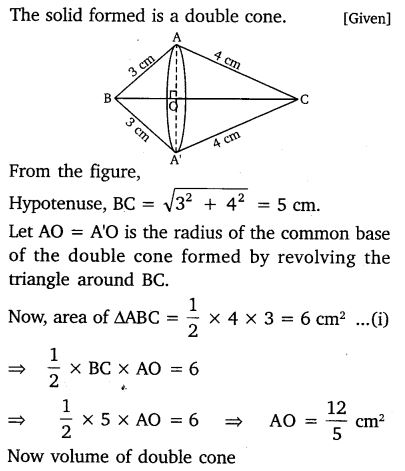

Ex 13.5 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
A cistern measuring 150 cm x 120 cm x 110 cm has 129600 cm3 water in it. Porous bricks are placed in the water until the cistern is full to the brim. Each brick absorbs one seventeenth of its own volume of water. How many bricks can be put in without overflowing the water, each brick being 22.5 cm x 7.5 cm x 6.5 cm?
Solution:
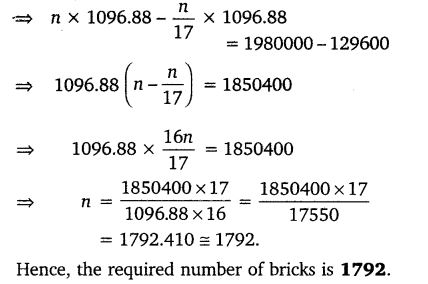
Ex 13.5 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
In one fortnight of a given month, there was a rainfall of 10 cm in a river valley. If the area of the valley is 7280 km, show that the total rainfall was approximately equivalent to addition to the normal water of three rivers each 1072 km long. 75 m wide and 3 m deep.
Solution:
Ex 13.5 Class 10 Maths Question 5.
An oil funnel made of tin sheer consists of a 10 cm long cylindrical portion attached to a frustum of a cone. If the total height is 22 cm, diameter of the cylindrical portion is 8 cm and the diameter of the top of the funnel is 18 cm, find the area of the tin sheet required to make the funnel.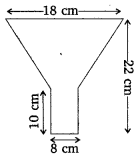
Solution:











