NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles Ex 10.1
Ex 10.1 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
How many tangents can a circle have?
Solution:
There can be infinitely many tangents to a circle.
Ex 10.1 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) A tangent to a circle intersects it in ………… point(s).
(ii) A line intersecting a circle in two points is called a ………… .
(iii) A circle can have ………………. parallel tangents at the most.
(iv) The common point of a tangent to a circle and the circle is called ……….. .
Solution:
Ex 10.1 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
A tangent PQ at a point P of a circle of radius 5 cm meets a line through the centre O at a point Q so that OQ = 12 cm. Length PQ is
(a) 12 cm
(b) 13 cm
(c) 8.5 cm
(d)
Solution: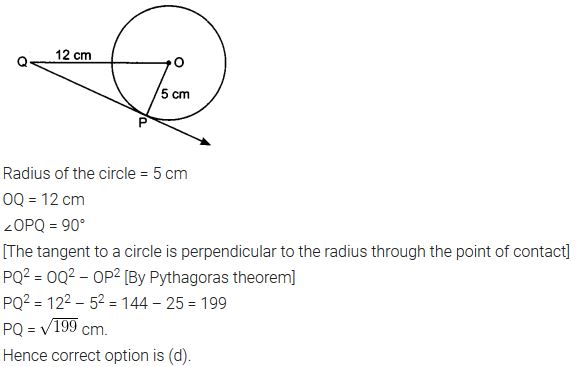
Note: PQ = √119
Ex 10.1 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
Draw a circle and two lines parallel to a given line such that one is a tangent and the other, a secant to the circle.
Solution: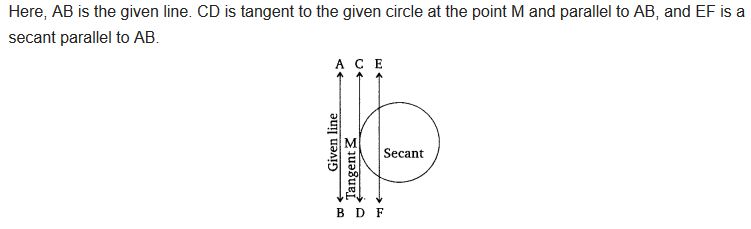
Class 10 Maths Circles Mind Map
Introduction
A circle is a set of all points in a plane at a fixed distance from a fixed point in a plane. The fixed point is called the centre of the circle. The fixed distance is called the radius of the circle.
Line and a Circle
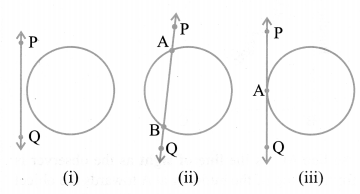
In Fig. (i), the line PQ and the circle have no common point. In this case, PQ is called a non-intersecting line with respect to the circle. In Fig. (ii), there are two common points A and B that the line PQ and the circle have. In this case, we call the line PQ a secant of the circle. In Fig. (iii), there is only one point A which is common to the line PQ and the circle. In this case, the line is called a tangent to the circle.
Tangent
A tangent to a circle is a straight line which touches the circle at only one point. The point where the tangent touches the circle is called point of contact of the tangent to the circle.
A tangent to a circle is a special case of a secant, when the two ends points of its corresponding chord coincides.
Theorem: Tangent at any point on a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.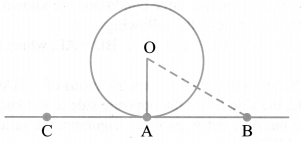
CB is the tangent to the given circle touching at A and OA is the radius.
∴ ∠OAB = 90°
(i) At any point on the circle there can be one and only one tangent.
(ii) The line containing the radius through the point of contact is called the normal to the circle at the point.
Number of Tangents from a Point to Circle
(i) No tangent can be drawn from the point lying inside the circle, as shown in fig. (i)
(ii) One and only one tangent can be drawn from a point lying on the circle, as shown in fig. (ii)
(iii) Only two tangents can be drawn from an exterior point to a circle, as shown in fig. (iii)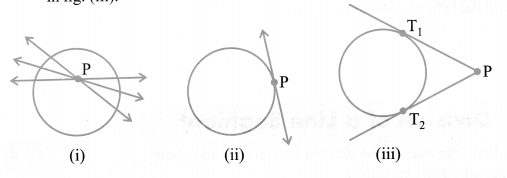
Length of a Tangent
The length of the segment of a tangent from an external point to the point of contact with the circle is called the length of the tangent
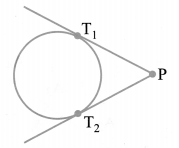
In the given figure, T1 and T2 are the points of contact of the tangents PT1 and PT2 respectively from the external point P.
Theorem Related to Length of Tangents From the External Points
The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
i.e.,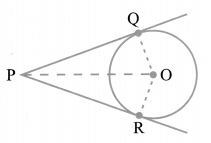
Here, PQ and PR are the two tangents drawn from P to the circle
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles Ex 10.2
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles Ex 10.2 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles Ex 10.2
In Q.1 to 3 choose the correct option and give justification.
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
From a point Q, the length of the tangent to a circle is 24 cm and the distance of Q from the centre is 25 cm. The radius of the circle is
(a) 7 cm
(b) 12 cm
(c) 15 cm
(d) 24.5 cm
Solution: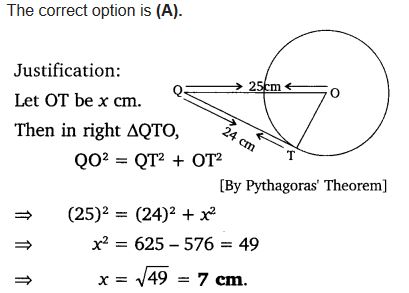
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
In figure, if TP and TQ are the two tangents to a circle with centre O so that ∠POQ = 110°, then ∠PTQ is equal to
(a) 60°
(b) 70°
(c) 80°
(d) 90°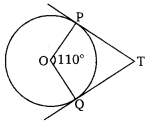
Solution: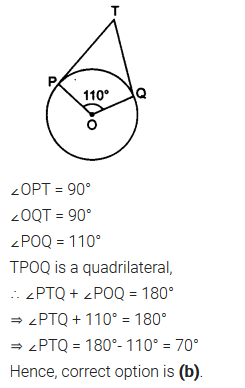
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
If tangents PA and PB from a point P to a circle with centre O are inclined to each other at angle of 80°, then ∠POA is equal to
(a) 50°
(b) 60°
(c) 70°
(d) 80°
Solution: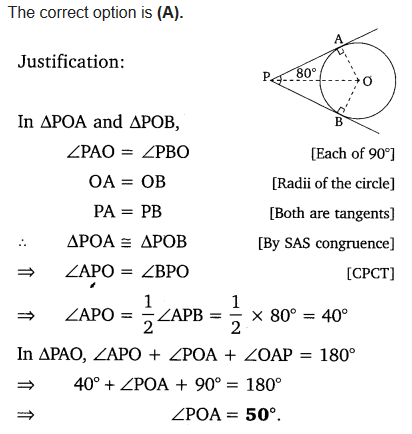
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
Prove that the tangents drawn at the ends of a diameter of a circle are parallel.
Solution: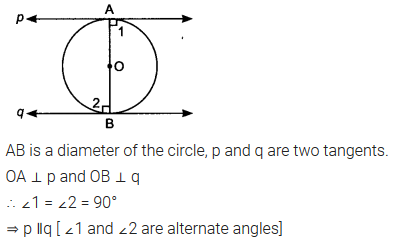
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 5.
Prove that the perpendicular at the point of contact to the tangent to a circle passes through the centre.
Solution: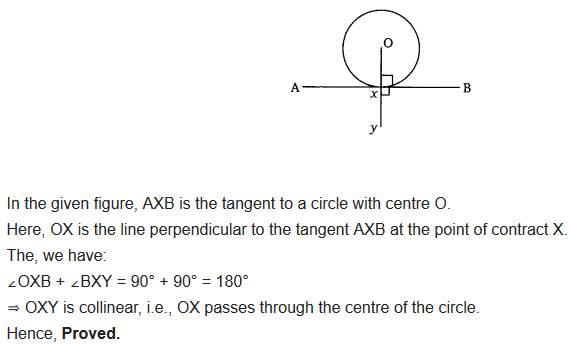
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 6.
The length of a tangent from a point A at distance 5 cm from the centre of the circle is 4 cm. Find the radius of the circle.
Solution: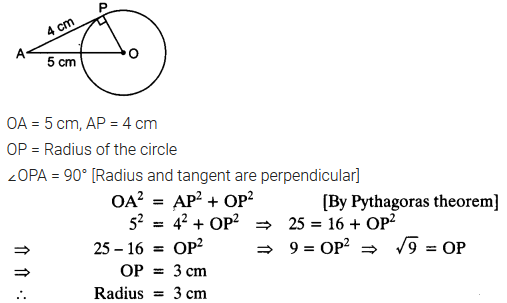
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 7.
Two concentric circles are of radii 5 cm and 3 cm. Find the length of the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle.
Solution: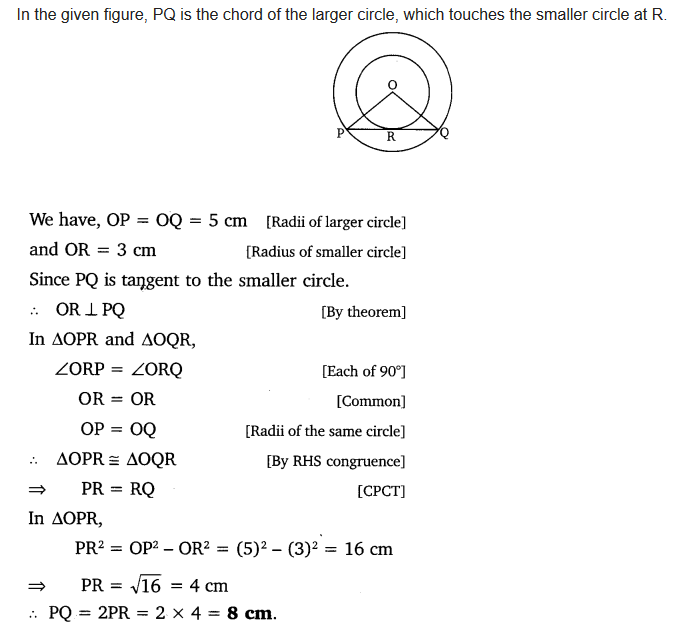
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 8.
A quadrilateral ABCD is drawn to circumscribe a circle (see figure). Prove that AB + CD = AD + BC.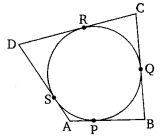
Solution: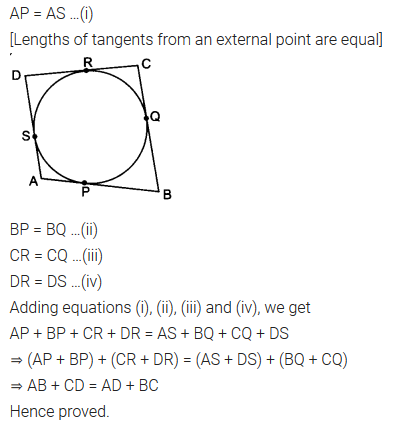
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 9.
In figure, XY and X’Y’ are two parallel tangents to a circle , x with centre O and another tangent AB with point of contact C intersecting XY at A and X’Y’ at B. Prove that ∠AOB = 90°.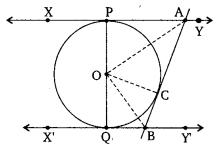
Solution: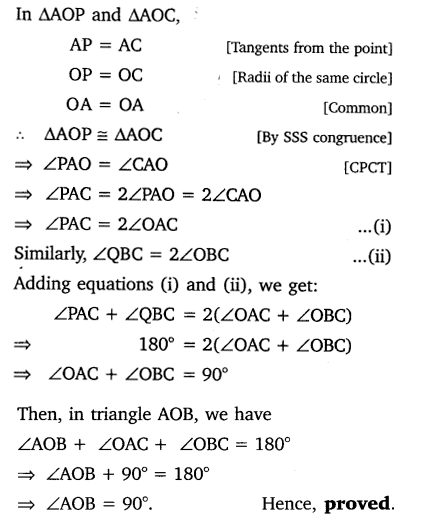
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 10.
Prove that the angle between the two tangents drawn from an external point to a circle is supplementary to the angle subtended by the line segment joining the points of contact at the centre.
Solution: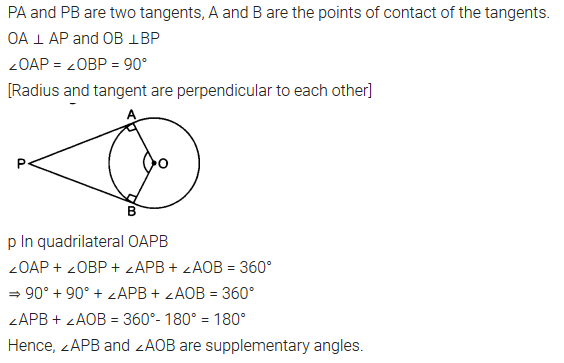
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 11.
Prove that the parallelogram circumscribing a circle is a rhombus.
Solution: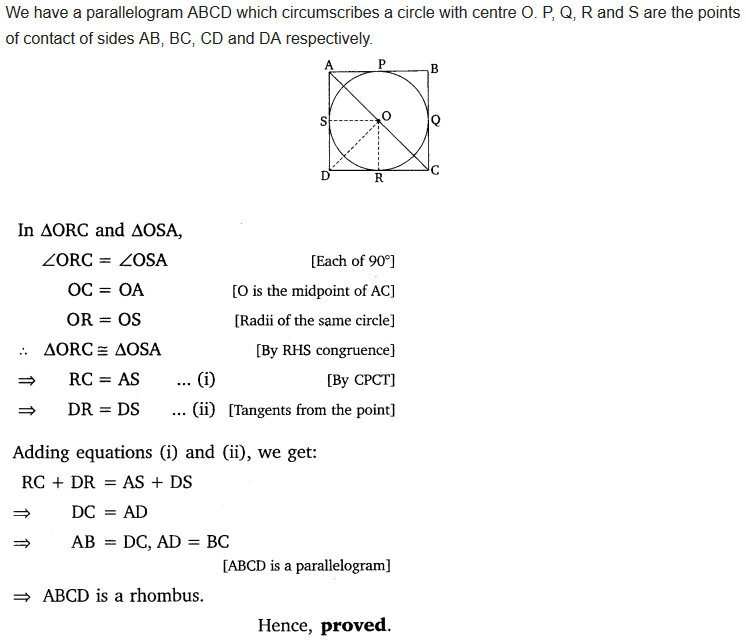
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 12.
A triangle ABC is drawn to circumscribe a circle of radius 4 cm such that the segments BD and DC into which BC is divided by the point of contact D are of lengths 8 cm and 6 cm respectively (see figure). Find the sides AB and AC.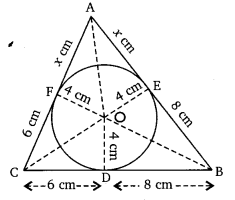
Solution: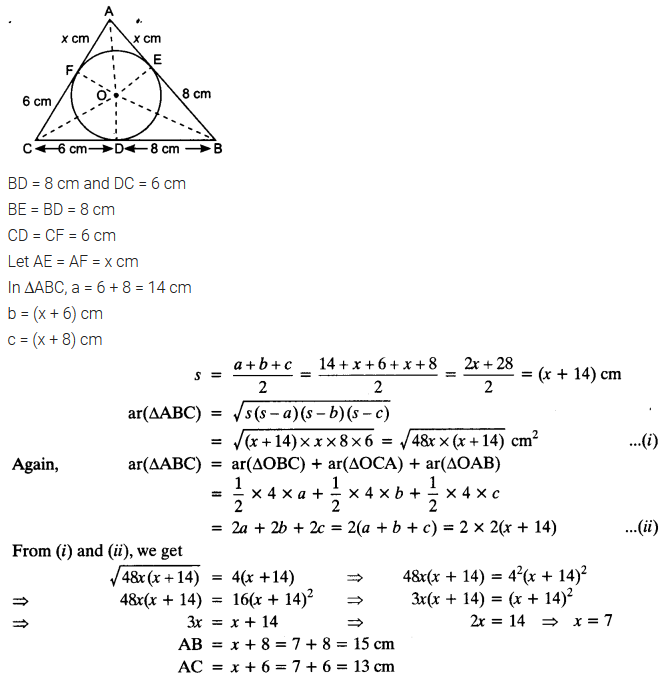
Ex 10.2 Class 10 Maths Question 13.
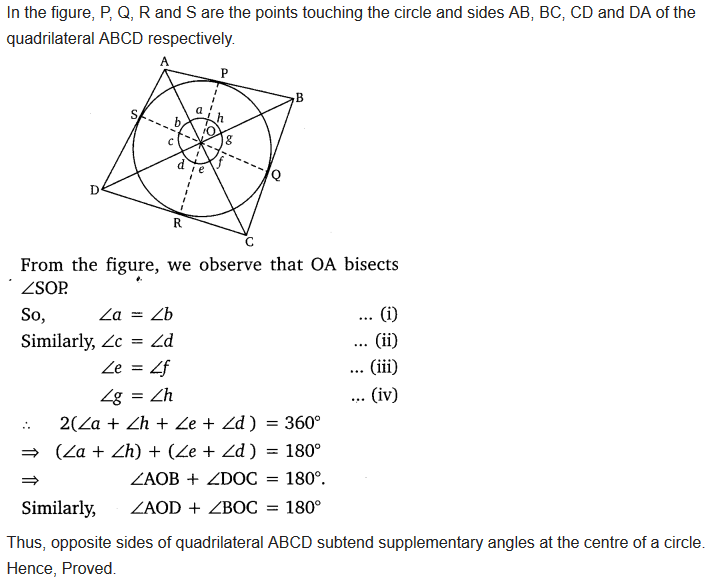
Prove that opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle subtend supplementary angles at the centre of the circle.
Solution: