Geography Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 17 Mineral and Energy Resources
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Classify mineral on the basis of chemical and physical properties. (All India 2017)
Answer:
On the basis of chemical properties and physical properties, a mineral is classified into the following:
- Metallic minerals
- Non-metallic minerals
Question 2.
Explain one reason for the import of petroleum and its products in large quantities in India. (All Indio 2016)
Answer:
The import of petroleum and its products in large quantities in India is due to the following reasons:
More vehicle purchase
- Increased use of diesel for irrigation due to weak monsoon.
- Rising industrialization.
Question 3.
Name any two ferrous minerals other than iron-ore. (All India 2011)
Answer:
Two ferrous minerals are:
- Manganese
- Nickel
Question 4.
Name the place of Maharashtra, where an atomic power station is located. (All India 2010)
Answer:
The atomic power station of Maharashtra is located in Tarapur.
Question 5.
Name the river-valley where Gondwana coal fields of India are located, (AH Indio 2008)
Answer:
Gondwana coal-fields are located in Damodar Valley.
Question 6.
Which are the two main types of iron-ore found in India? (AH India 2008)
Answer:
The two main types of iron-ore found in India are:
- Hachette
- Magnetite
3 Marks Questions
Question 7.
“The promotion of the use of non-conventional sources of energy in India is the need of the hour.” Support the Statement. (HOTS; Delhi 2016)
Answer:
It is true that the promotion of the use of non-conventional sources of energy in India is the need of the hour due to the following reasons:
- Unlike conventional sources of energy, most of the non-conventional energy sources are cheaper and renewable. The overall limitation and scarcity of fossil fuels have given rise to the urgent need for exploiting alternative energy sources.
- Power from non-conventional and renewable sources is must in order to reduce carbon dioxide emissions of the coal-based power plants. It is exhaustible in nature and environment-friendly.
- Locally available non-conventional and renewable power resources can meet localized rural energy with minimum transportation cost.
Question 8.
Explain the significance of bio-energy to humankind in India, (AH India 2016)
Answer:
The significance of bio-energy to humankind can be understood through the following points:
- Bio-energy is a result of the processing of biological products such as agricultural residues, municipal, industrial and other wastes.
- Bio-energy can be used by converting it into electricity or electrical energy, heat energy or gas for cooking food.
- Apart from deriving energy, it can also solve the problem of garbage and waste in urban areas because energy can also be derived from these.
- It can improve the economic life of rural peoples and also reduce environmental pollution pressure on fuelwood and enhance self-reliance.
Question 9.
Explain any three main characteristics of the mineral resources of India. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
The major characteristics of mineral resources are as follows:
- Their distribution over the earth surface is uneven i.e. some regions may have rich in minerals whereas others may be lack behind in availability of minerals,
- Minerals of good quality are less in amount and minerals of low quality are more in the amount on earth i.e. quality and quantity of minerals have an inverse relationship.
- Minerals are exhaustible, i.e. once used they can’t be used again. Minerals take a long time to develop geologically and once they exhausted they cannot be available at that time for use.
Question 10.
Give two advantages of copper’. Mention four copper mining areas of India. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Copper is a non-ferrous mineral found in India. It has various advantages such as:
- Copper due to its allowable, malleable and ductile properties mostly use in the electrical industry for making wires, electric motors, transformers, and generators.
- To give strength, copper is also mixed with gold in making jewelry. Four copper producing states of India are:
- Copper deposits mainly found in Singhbhum district in Jharkhand.
- It is found in Balaghat district of Madhya Pradesh.
- Alwar, Jhunjhunu, Bhilwara and Udaipur districts of Rajasthan are producers of copper.
- Agni Gundala in Guntur district of Andhra Pradesh. Chitradurga and Hassan districts of Karnataka and South Arcot district of Tamil Nadu are other producers of copper ore.
Question 11.
Give two advantages of Manganese. Mention four manganese producing states of India. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
The two advantages of manganese are as follows:
- Manganese is a ferrous mineral found in India. It is used as a raw material in the iron and steel industry for the smelting of iron-ore.
- It is also used in the manufacturing of ferroalloys. Four manganese producing states of India are:
Odisha It is the largest manganese producer in India. Important mines are located in the districts of Bonai, Kendujhari, Sundergarh, Gangpur, Koraput, Kalahandi and Bolangir.
Karnataka Important mines are located in Dharwar, Biliary, Belgaum, North Canara, Chikmagalur, Shimoga, Chitradurga, and Tumkur districts.
Maharashtra Manganese mines are found in Bhandara, Nagpur and Ratnagiri.
Madhya Pradesh Its mines are located in the belt of Balaghat, Chhindwara, Nimar, Mandla and Jhabua districts.
Question 12.
Give two advantages of wind energy.’ Mention four states for India having favorable conditions for the development of wind energy. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Wind energy is another non-conventional source of energy. The two advantages of wind energy are as follows:
- Wind energy is a clean fuel source. It does not pollute the air as compared to conventional sources.
- Wind power is one of the lowest-cost renewable energy technologies available today. Even without government subsidies, wind power is a low-cost fuel in many areas of the country.
Four wind power producing states of India are:
- Rajasthan
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
- Karnataka
Question 13.
Describe the uneven distribution of mineral and energy resources in India by giving suitable examples. (HOTS; Delhi 2012)
Answer:
India is a rich country in terms of minerals. Most of the metallic minerals occur in the Peninsular Plateau region in the old crystalline rocks. River valleys of Damodar, Sone, Mahanadi, and Godavari have over 97% of coal reserves in India.
Sedimentary basins of Assam and off-shore region in the Arabian Sea (Gujarat and Mumbai High) are famous for their crude petroleum reserves. The area to the east of a line linking Mangalore and Kanpur has most of the major mineral resources of India.
A mineral is mainly concentrated in three broad belts, namely:
- The North-Eastern Plateau region
- The South-Western Plateau region
- The North-Western region
Question 14.
Describe the broad belts of minerals in India. (All India 2012)
Answer:
The mineral belts of minerals in India are as follows:
The North-Eastern Plateau Region This belt includes the regions of Chotanagpur (Jharkhand), Odisha plateau, West Bengal and parts of Chhattisgarh. Important minerals are iron ore, coal, manganese, bauxite, mica.
The South-Western Plateau Region This belt includes Karnataka, Goa and contiguous uplands of Tamil Nadu and Kerala. Ferrous metals and bauxite are concentrated here along with high-grade iron-ore, manganese, and limestone. Neyveli has lignite coal deposit. Deposits of Monazite sand and thorium are found in Kerala. Mines of iron-ore are located in Goa.
The North-Western Region Minerals of this belt are associated with the Dharwar system of rocks which are found in the Aravali in Rajasthan and parts of Gujarat. Major minerals are copper and zinc. Rajasthan is rich in building stones i.e. sandstone, granite, marble, fuller’s earth, and gypsum
Question 15.
“Conservation of minerals is more important than other resources”. Explain by giving three arguments. (HOTS; All Indio 2012)
Answer:
Conservation of minerals is more important than other resources due to the following reasons:
- Minerals are important to conserve as industries and agriculture are dependent completely on minerals and the substance manufactured from them.
- We are rapidly consuming mineral resources that require millions of years to be renewed.
- Workable minerals are in insufficient quantities, for e.g. only 1% of the earth’s crust.
- Due to a decrease in good quality and they come from great depths, the costs of mineral extraction are increasing.
- Economic and industrial development depends on minerals.
Question 16.
Explain any three methods of conservation of minerals resources in India. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
There are some methods through which we can conserve mineral resources:
- Adoption of renewable resources in place of exhaustible resources like solar power, wind, wave, geothermal energy can save our non-renewable resources.
- Use of recycling scrap metals should be encouraged. It can save the mining of newer metals. In India, the scope of some scarce metallic minerals like zinc, copper, lead are useful because India is lacking‘behind in these minerals.
- Substitute for some precious and scarce-metals should be encouraged. It can reduce their consumption.
Question 17.
Why is conservation of minerals essential in India? How can we conserve them? Explain in two points. (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
Conservation of minerals is more important than other resources due to the following reasons:
- Minerals are important to conserve as industries and agriculture are dependent completely on minerals and the substance manufactured from them.
- We are rapidly consuming mineral resources that require millions of years to be renewed.
- Workable minerals are in insufficient quantities, for e.g. only 1% of the earth’s crust.
- Due to a decrease in good quality and they come from great depths, the costs of mineral extraction is increasing.
- Economic and industrial development depends on minerals.
There are some methods through which we can conserve mineral resources:
- Adoption of renewable resources in place of exhaustible resources like solar power, wind, wave, geothermal energy can save our non-renewable resources.
- Use of recycling scrap metals should be encouraged. It can save the mining of newer metals. In India, scope of some scarce metallic minerals like zinc, copper, lead are useful because India is lacking‘behind in these minerals.
- Substitute for some precious and scarce-metals should be encouraged. It can reduce their consumption.
5 Marks Questions
Question 18.
Classify minerals into two groups on the basis of chemical and physical properties and give one example of minerals of each group. Mention any two features of the three minerals belts of India. (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
Minerals are classified on the basis of their physical properties and chemical properties such as:
Metallic Minerals
Metallic minerals are those that are rich in metals and a source to procure a variety of metals like copper, gold, iron, etc. Bauxite, iron-ore are some examples of metallic minerals. There are two types of metallic minerals i.e. ferrous and non-ferrous.
Non-Metallic Minerals
Non-metallic minerals are those that do not have metal components. For features of the three mineral belts of India,
The mineral belts of minerals in India are as follows:
The North-Eastern Plateau Region This belt includes the regions of Chotanagpur (Jharkhand), Odisha plateau, West Bengal and parts of Chhattisgarh. Important minerals are iron ore, coal, manganese, bauxite, mica.
The South-Western Plateau Region This belt includes Karnataka, Goa and contiguous uplands of Tamil Nadu and Kerala. Ferrous metals and bauxite are concentrated here along with high-grade iron-ore, manganese, and limestone. Neyveli has lignite coal deposit. Deposits of Monazite sand and thorium are found in Kerala. Mines of iron-ore are located in Goa.
The North-Western Region Minerals of this belt are associated with the Dharwar system of rocks which are found in the Aravali in Rajasthan and parts of Gujarat. Major minerals are copper and zinc. Rajasthan is rich in building stones i.e. sandstone, granite, marble, fuller’s earth, and gypsum
Question 19.
What is the use of manganese? Describe the state-wise distribution of manganese in India. (All Indio 2009)
Answer:
Manganese is used as follows:
- Used as a raw material in the iron and steel industry for the smelting of iron-ore.
- Used in the manufacturing of ferroalloys.
Statewide distribution of manganese are as follows:
- Manganese is found in the rocks of all geological formations in India. But large manganese deposits are found in the rocks of Dharwar system.
- Odisha is the largest manganese producer in India. A central part of the iron-ore belt of India has most of the manganese mines of Odisha. These mines are located in the districts of Bonai, Kendujhar, Sundergarh, Gangpur, Koraput, Kalahandi and Bolangir in Odisha.
- Karnataka is also known for its manganese mines and production. Dharwar, Bellary, Belgaum, North Canara, Chikmagalur, Shimoga, Chitradurga, and Tumkur are districts having major manganese mines.
- Manganese mines of Maharashtra are situated away from iron and steel plants. This is the main disadvantage of Bhandara. Nagpur and Ratnagiri have manganese deposits.
- Most of the manganese mines are located in the belt of Balaghat, Chhindwara-Nima, Mandla, and Jhabua. districts in Madhya Pradesh.
- Other producer states of manganese are Andhra Pradesh, Goa, and Jharkhand.
Map-Based Questions
Question 20.
Locate and label the following on the given political outline map of India with appropriate symbols.
(i) Mayurbhanj- an iron-ore mining area. (Delhi 2016,2013)
(ii) An oil refinery in Karnataka state. (Delhi 2016, All Indio 2015)
(iii) A major copper mining area in Southern Rajasthan. (All Indio 2016)
(iv) An oil refinery in Haryana. (Delhi 2015)
Answer: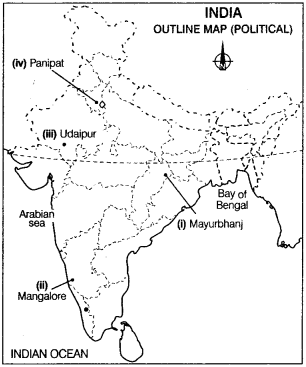
Question 21.
Locate and label the following on the given political outline map of India with appropriate symbols.
(i) Mayurbhanj an iron-ore mining area. (Delhi 2016. 2013)
(ii) A copper mining area of Southern Jharkhand. (Delhi 2013)
Answer: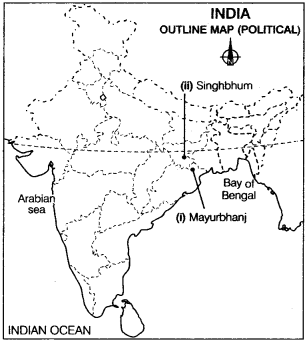
Question 22.
In the given political outline map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols.
(i) An iron ore mine of Karnataka. (Delhi 2012)
(ii) Name the place where an oil refinery is located in Haryana. (Delhi 2012)
Answer: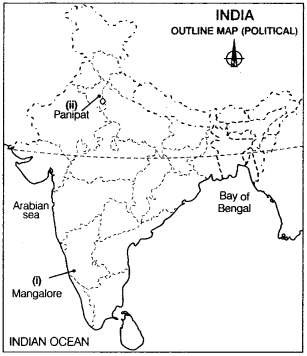
Question 23.
In the given political outline map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols.
(i) The oil refinery located in West Bengal. (All India 2011, Delhi 2009)
(ii) The oil refinery located in Bihar. (All India 2011, Delhi 2009)
Answer: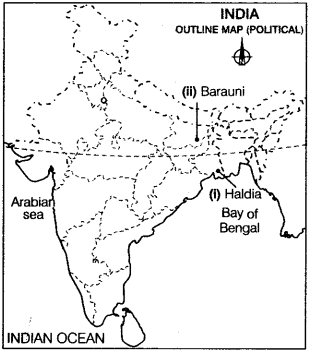
Question 24.
On the given political outline map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols.
(i) Singareni coal mines. (All India 2009)
(ii) An oil refinery located in Bihar. (All Indio 2011, Delhi 2009)
Answer: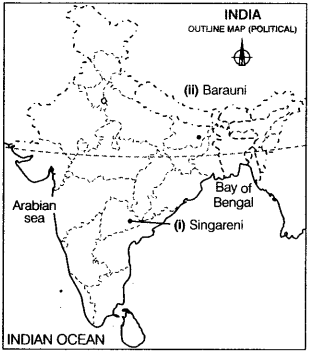
Value Based Questions
Question 25.
Electricity is one of the greatest inventions of all times. It is mostly generated by using coal, natural gas, and petroleum, which are exhaustible resources. Can you imagine a human society without electricity? This may happen in the future when all energy resources will be exhausted. Explain the values that can change this possible darkness scenario.
(All India 2015)
Answer:
Energy resources are very important as well as scarce for humankind as most of the work is done with the help of these resources, e.g. coal, natural gas, petroleum, and nuclear energy. One can not imagine a human society without these.
But at which rate these are consumed it is possible that these will be exhausted soon. So, we have to take great care of these resources through the following steps:
- Maximum utilization of renewable energy resources i.e. solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy, geothermal energy, etc.
- Create awareness among people about the judicious use of these resources.
- Promote the concept of sustainable development.
- Try not to waste these scarce and valuable resources.
Question 26.
Explain any three social and economic values which encourage us to use more and more non-conventional sources of energy. (All India 2014)
Answer:
Non-conventional energy sources are the alternatives to conventional sources of energy as former are exhaustive in nature and take longer time i.e. million years to replenish them.
So, it is important for us to adopt some values in our lives to save these precious sources, for e.g:
- Create awareness about sustainable development and the use of non-conventional sources.
- Try to inculcate the habit among masses, not to waste these sources and save for future generation also.
- Create awareness about cost-effective.
- More pollution in the environment i.e. water, air, land and soil pollution, need high technology to combat such situations which is very costly.
Question 27.
“The promotion of the use of non-conventional sources of energy in India is the need of the hour”. Which value is required to use the non-conventional sources of energy?
Answer:
Values which are required to use the non-conventional sources are:
- Sustainable development ‘
- Social dependence
- Public awareness
Question 28.
“Adoption of renewable resources in place of exhaustible resources like solar power, wind, geothermal energy can save our non-renewable resources”.
Which value will lead to saving our non-renewable resources?
Answer:
Values lead to saving our non-renewable resources are:
- Community awareness
- New technique
- Sustainable development











